Dec06

The choice between a TPU and a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) for AI workloads often comes down to a trade-off between specialization (TPU) and versatility (GPU). The TPU's role in future AI is best understood in comparison to its dominant competitor:
The pursuit of more sophisticated Artificial Intelligence, from multi-step Agentic AI to the eventual realization of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), is fundamentally a pursuit of compute. At the heart of this drive is the Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), Google's custom-designed Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). By trading the general-purpose flexibility of traditional CPUs and GPUs for extreme specialization in deep learning's linear algebra, TPUs have created the necessary infrastructure for training and deploying the massive models that underpin today's and tomorrow's most ambitious AI systems.
The core innovation of the TPU lies in its architecture, which is built around the systolic array. This design allows data, in the form of tensors (multidimensional arrays), to flow rhythmically through a grid of thousands of multiply-accumulate units. This highly optimized, assembly-line approach drastically reduces the need for constant, slow memory access, bypassing the classic von Neumann bottleneck that constrains general-purpose processors.
This architectural choice yields three critical benefits:
The choice between a TPU and a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) for AI workloads often comes down to a trade-off between specialization (TPU) and versatility (GPU). The TPU's role in future AI is best understood in comparison to its dominant competitor:
| Feature | Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) | Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) |
| Design/Architecture | ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit). Uses a Systolic Array designed exclusively for dense matrix multiplication. | General-Purpose Processor. Uses thousands of programmable cores. |
| Primary Focus | Specialized for AI/ML. Optimized for tensor algebra, particularly for training and inference of large neural networks. | Versatile. Used for graphics rendering, scientific computing, and general AI/ML. |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher Performance per Watt for AI workloads. | Less efficient for dense matrix math, with higher overall power consumption per chip. |
| Flexibility | Limited. Optimized for specific frameworks (like TensorFlow and JAX). | High. Broad support for all major frameworks (PyTorch, TensorFlow, etc.) and custom operations. |
| Scalability | Designed for massive scale via TPU Pods (thousands of interconnected chips). | Scales well with interconnects but is generally limited to smaller clusters. |
For workloads that perfectly fit the deep learning model and use the optimized software stack, TPUs often offer significantly better performance per dollar and energy efficiency than contemporary GPUs. For specific workloads, such as large language model training, recent TPU generations have been shown to offer superior value. However, GPUs remain the industry standard for their unmatched flexibility and broad ecosystem, making them the preferred choice for researchers and tasks requiring custom operations or diverse computational needs. The ultimate trend is that TPUs are the powerhouses for achieving extreme scale in training frontier models, while GPUs maintain dominance through versatility and accessibility.
The specialized capabilities of TPU are crucial for advancing AI beyond its current state.
Agentic AI systems, which rely on AI agents to plan, execute multi-step workflows, and coordinate with tools, are directly enabled by TPU efficiency. TPUs accelerate the training and continuous fine-tuning of the competent foundation models that serve as the agents' cognitive core. Furthermore, for agentic workflows involving dozens or hundreds of sequential model calls, TPUs provide the high throughput and low latency necessary for cost-efficient inference at scale, making large fleets of active agents economically viable.
The realization of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is often framed as a problem of scale, requiring models exponentially larger than those available today. TPUs provide the maximum available computational fabric today through the TPU Pod architecture, enabling unprecedented numbers of parameters to capture the vast, interconnected knowledge and emergent reasoning abilities required for AGI. By drastically reducing the time needed to train a massive experimental model, TPUs accelerate the entire research pipeline—a vital process for exploring novel architectures and training techniques that may lead to an AGI breakthrough.
In conclusion, the TPU is more than just a fast chip; it is an economic and architectural blueprint for massive-scale, energy-efficient AI. It is the powerhouse that trains the large language models, enabling today's Agentic AI workflows and providing the essential compute density required to move closer to the era of AGI. Without this specialized hardware foundation, the current trajectory of rapid AI advancement would be severely constrained by the limitations of general-purpose computing.
Keywords: Generative AI, Open Source, Agentic AI
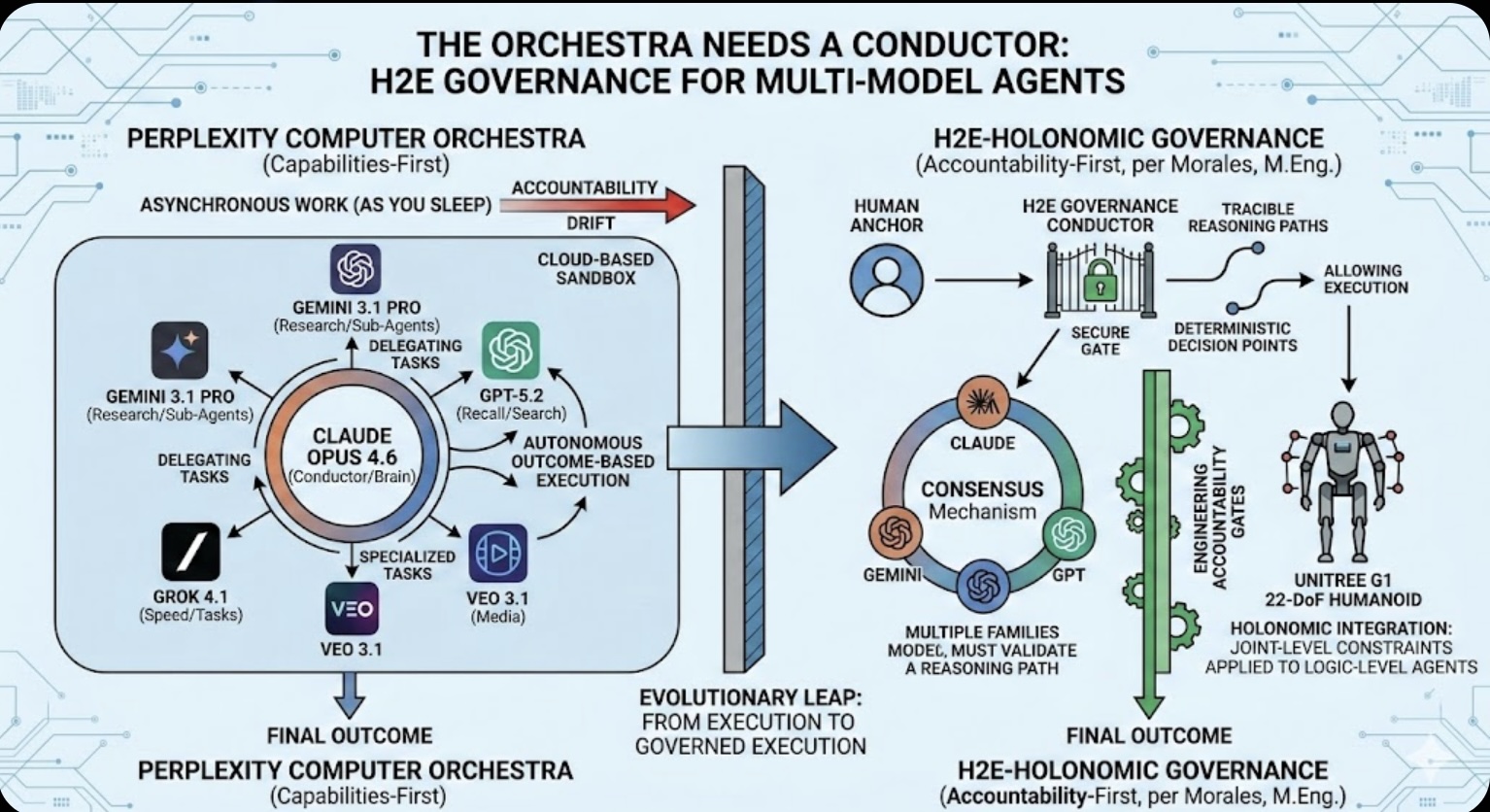 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business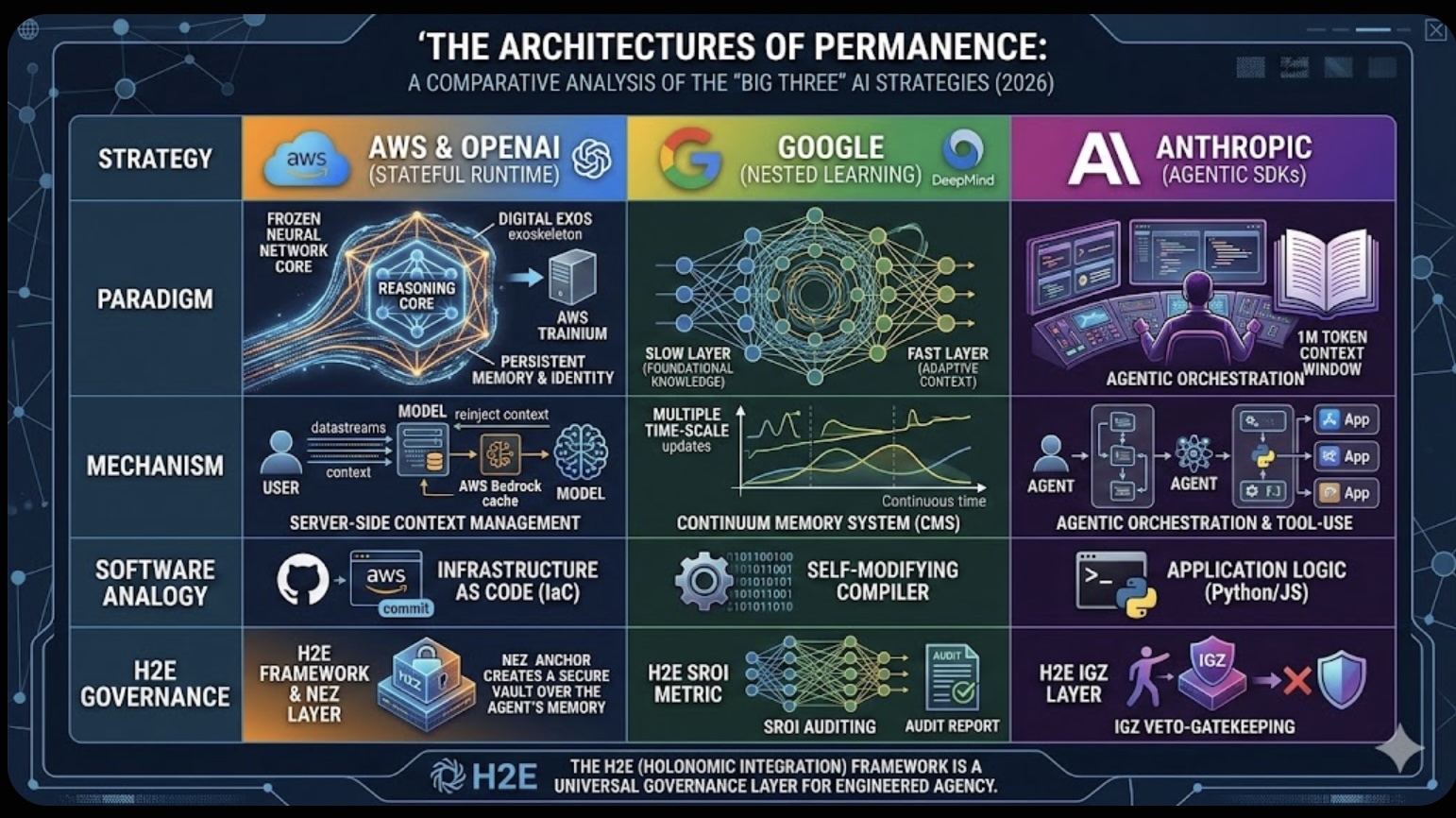 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026