Nov17

Agentic AI as the New Cyber Battle-Ground
Prediction: Autonomous (“agentic”) AI — systems that act with minimal human intervention — will be central in both attacks and defense.
Implication: Attackers will use AI bots to run reconnaissance, move laterally, and exfiltrate data; defenders must deploy AI agents to monitor, detect, and contain threats. Security teams need to simulate “agents in the wild” to test unexpected, emergent behaviors.
Quantum Computing Threat Accelerates
Prediction: 2026 will mark a tipping point for quantum-related risk.
Implication: Stolen data today may be decrypted later (“harvest now, decrypt later”). Legacy encryption systems (e.g., RSA, ECC) will be increasingly vulnerable. Organizations must inventory their crypto assets, adopt post-quantum or hybrid cryptography, and properly manage key deletion and archival.
Rise of Deepfakes and Synthetic Identities
Prediction: Deepfake audio/video and synthetic identities will be used more aggressively by threat actors.
Implication: Traditional identity verification (e.g., one-time checks) will be insufficient. Defense strategies should incorporate continuous authentication and behavioral anomaly detection. There's also a need to educate employees about “synthetic realism” and plan for legal/insurance coverage relating to identity spoofing.
Expanding Attack Surface via IoT, Edge, and Device Proliferation
Prediction: As IoT, edge computing, and 5G/6G expand, attackers will increasingly exploit weak embedded devices.
Implication: Devices with poor patching capabilities or default credentials will be prime targets. Edge clusters can become pivot points for lateral movement. Security must emphasize device lifecycle management (provisioning, patching, decommissioning), micro-segmentation, and a zero-trust mindset at the device level.
Cybercrime Organizes as Corporate-Class Businesses
Prediction: Cybercriminal groups will operate more like formal enterprises, with affiliate models, subscriptions, and full “service industries” around ransomware and extortion.
Implication: Treat threat actors not merely as “hackers” but as business competitors. Expect outsourced operations, “customer support” for ransomware victims, and professionalization. Organizations need to invest in resilience (not just prevention), leadership, and culture, and integrate business continuity, insurance, and legal strategies into their incident response planning.
Cybersecurity as a Strategic Business Pillar
Prediction: Companies that embed cybersecurity into their business strategy — not just treat it as IT overhead — will perform best.
Implication: CISOs (or equivalent) must be elevated to strategic business partners. Metrics should go beyond “threats blocked” to include resilience indicators: time-to-recover, adaptability, containment effectiveness. Cyber risk must be woven into board-level discussions, supply-chain coordination, threat intelligence sharing, and cultural change.
For more perspectives please also see: Cybersecurity 2026: 6 Forecasts and a Blueprint for the Year Ahead
By Chuck Brooks
Keywords: Cybersecurity
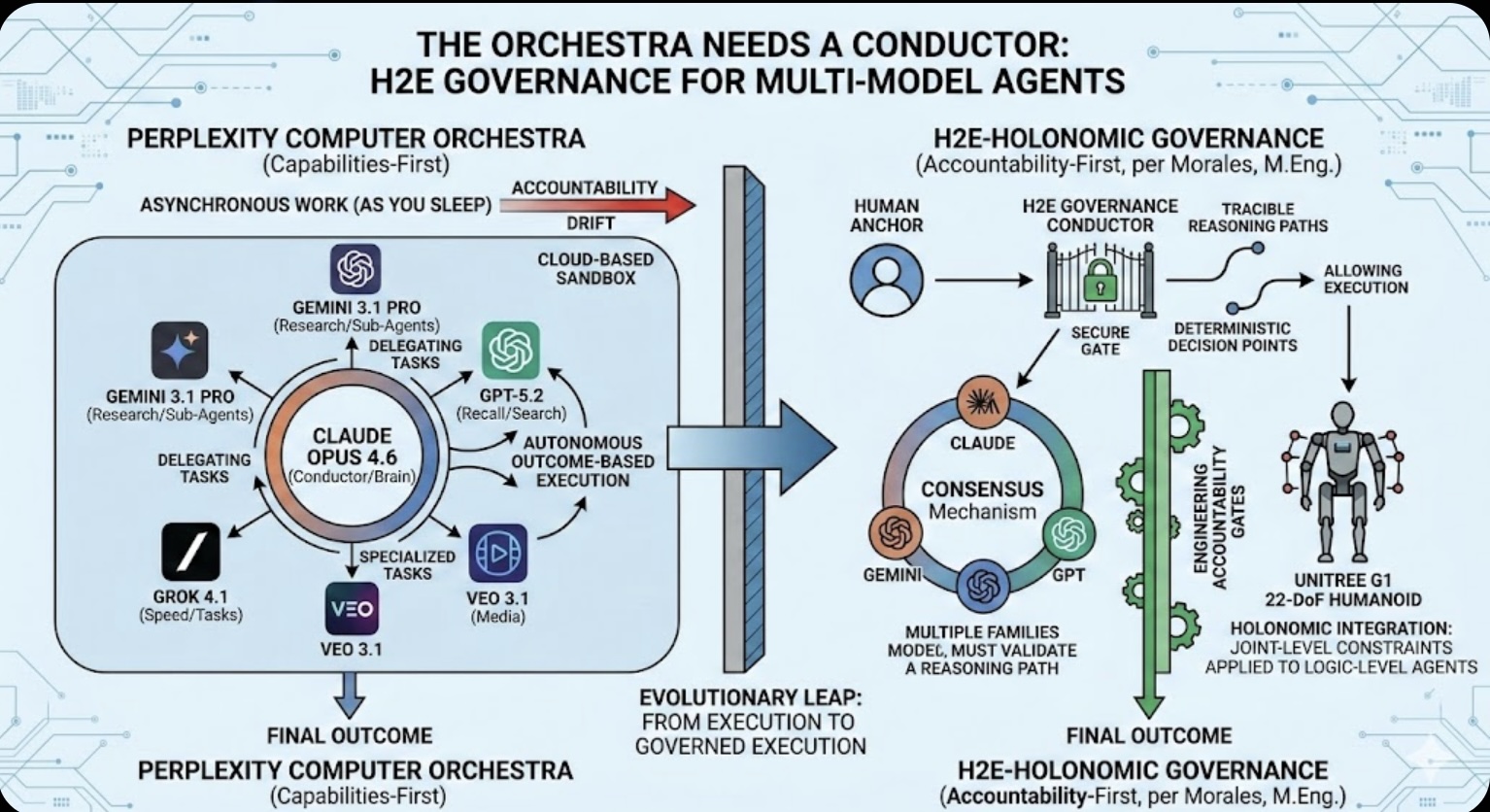 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business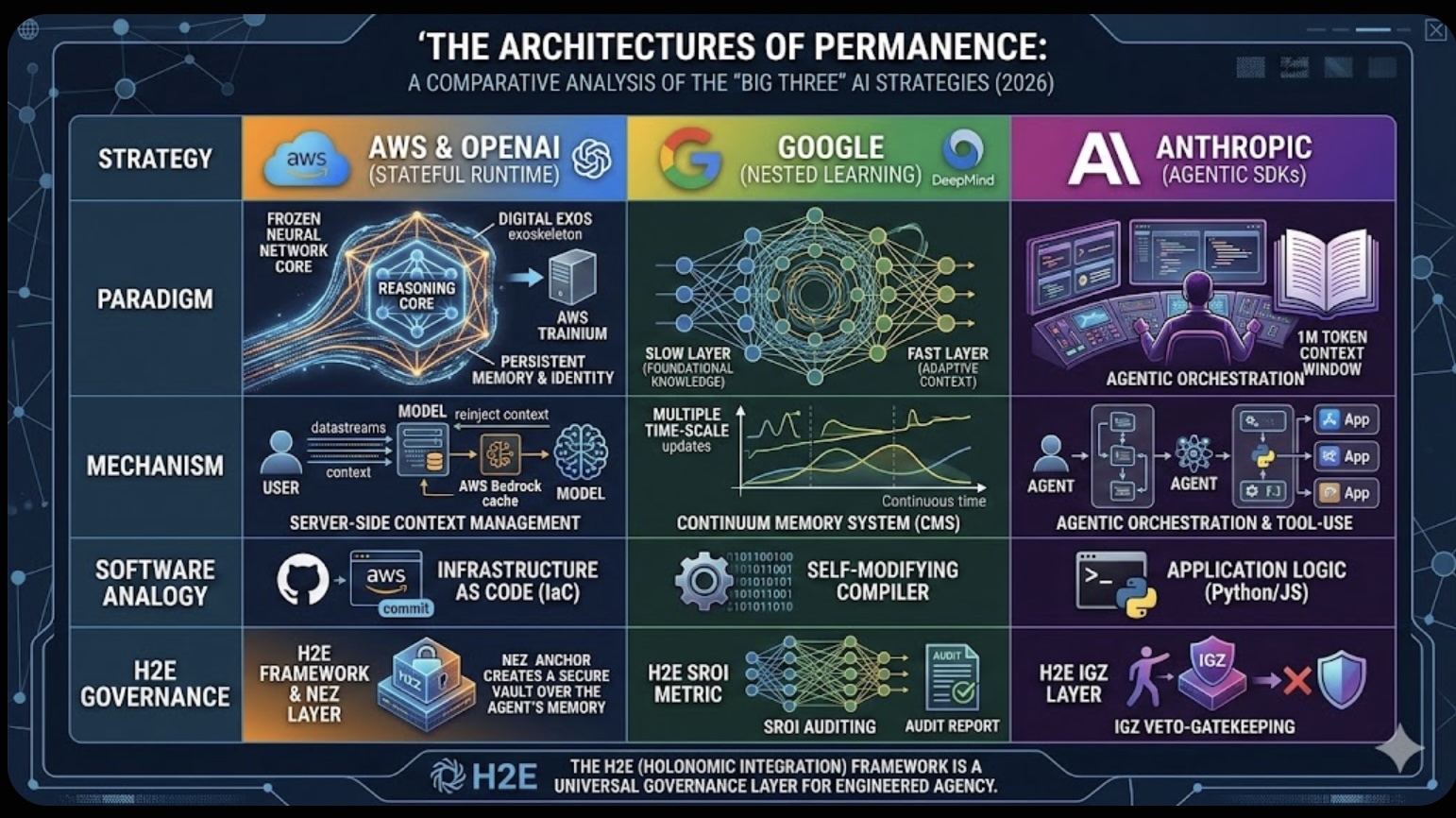 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026