Jan12

The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has shifted the focus of AI development from simple chatbots to autonomous "agents"—systems capable of reasoning, planning, and executing complex tasks by interacting with external tools. At the forefront of this evolution is NVIDIA's NeMo Agent Toolkit (NAT), an open-source library for building, profiling, and optimizing high-performance AI agent workflows. The provided demonstration notebooks illustrate a critical "Day 1" workflow: preparing standalone Python tools and seamlessly integrating them into a managed agentic system.
NAT serves as a framework-agnostic "glue" layer, allowing developers to connect various LLMs with specialized functional tools. Unlike monolithic systems, NAT encourages a modular approach. As demonstrated in the notebooks, the first step in building a NAT agent is creating "Standalone Tools"—standard Python functions that remain independent of the toolkit until they are registered. In these examples, the tools are designed for climate analysis, capable of loading NOAA temperature records, calculating statistical trends, and generating visualizations like annual anomaly plots.
Using Google Colab as the primary environment highlights the toolkit's accessibility and integration with cloud workflows. The notebooks leverage colab_env to manage secure environment variables, specifically the NVIDIA_API_KEY, which provides access to NVIDIA NIMs (Inference Microservices). By programmatically creating a local module (climate_tools_simple.py) and updating the system path, the demonstration shows how a temporary cloud environment can be transformed into a robust development platform for AI agents.
The demonstration notebooks are designed to showcase the versatility and framework-agnostic nature of NAT. A key goal of these demos is to prove that the same open-source toolkit can seamlessly manage both commercial and open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) within a unified workflow.
Dual-Model Integration Strategy
The notebooks achieve this by utilizing the same backend "Tools" and infrastructure while swapping the "Reasoning Engine" (the LLM):
Commercial LLM Integration: The first notebook focuses on integrating a commercial LLM, specifically GPT-4, as the reasoning engine. This demonstrates how NAT can act as a secure bridge for high-performance, proprietary models.
Open-Source LLM Integration: The second notebook, DEEPSEEK_NAT_DEMO_JAN2025.ipynb, focuses on integrating DeepSeek, a prominent open-source model. It shows that the toolkit can successfully deploy open-source models to perform the same complex data analysis tasks as their commercial counterparts.
DEEPSEEK_NAT_DEMO_JAN2025.ipynb: https://github.com/frank-morales2020/MLxDL/blob/main/DEEPSEEK_NAT_DEMO_JAN2025.ipynb
/NEMO_Equation_AAI_DEMO.ipynb: https://github.com/frank-morales2020/Cloud_curious/blob/master/NEMO_Equation_AAI_DEMO.ipynb
Consistent Toolkit, Different Models
By using the NeMo Agent Toolkit as the constant factor, the demos illustrate several technical advantages:
Unified Configuration: Both models use a similar YAML-based configuration (config.yml) to define the agent's behaviour and the tools it can access.
Shared Tooling: Both the GPT-4 and DeepSeek agents leverage the same standalone Python module (climate_tools_simple.py) for climate data loading, statistical analysis, and visualization.
Environment Management: Both demos utilize colab_env and NVIDIA_API_KEY to securely manage model access, whether connecting to NVIDIA-hosted open-source NIMs or commercial endpoints.
This approach emphasizes that NAT is a glue layer that allows developers to choose the best model for their specific needs—whether open-source for transparency or commercial for performance—without rebuilding their entire agentic infrastructure.
The true power of NAT is realized when these local Python functions are bridged with an LLM's reasoning capabilities. In the DeepSeek iteration of the demo, the agent follows a structured process to answer natural language queries like "Find the warmest year between 1980 and 2000":
Reasoning: It identifies the need for statistical analysis.
Tool Execution: It calls the find_extreme_years function from the standalone module.
Synthesizing: It processes the tool output to provide a clear, factual answer, such as identifying 1998 as the warmest year with a 0.79°C anomaly.
The NAT demonstration notebooks provide a blueprint for modern AI development. By separating the "brain" (the LLM) from the "hands" (the Python tools), and using NAT to orchestrate their interaction, developers can create reliable, verifiable, and highly specialized agents. Whether analyzing global climate trends or managing complex industrial data, NVIDIA's NeMo Agent Toolkit offers the necessary infrastructure to move AI from experimental code to impactful, real-world applications.
Keywords: Predictive Analytics, Generative AI, Agentic AI
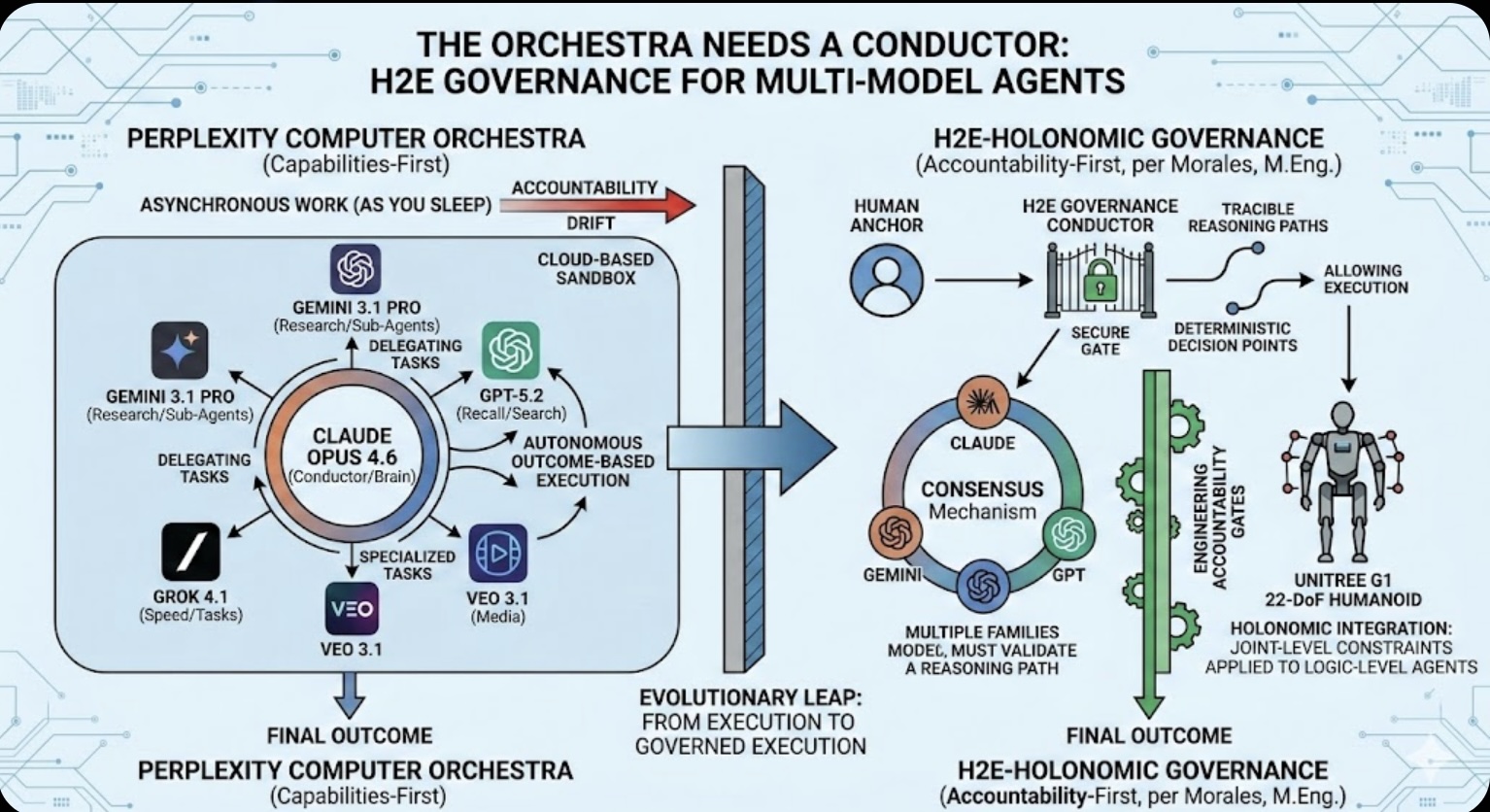 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business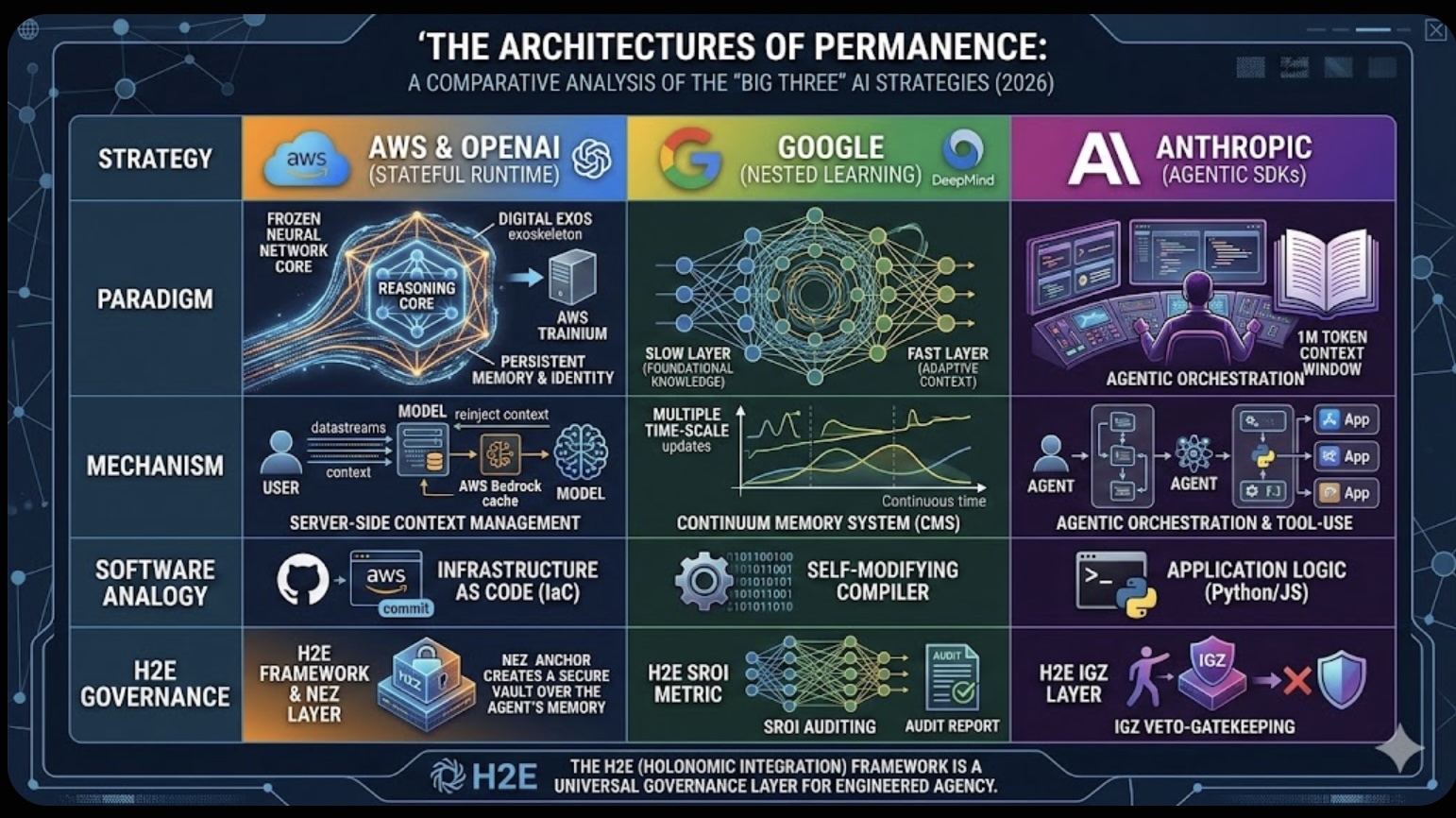 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026