

At CPF Coaching LLC, we go beyond individual coaching to offer comprehensive business advisory and security consulting services. This includes strategic planning, risk management, and implementing effective cybersecurity measures tailored to your business needs. We aim to protect your organization against emerging threats and are well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly digital landscape.
As a security practitioner, I assist businesses in tackling cybersecurity risks with minimal friction, enhancing resilience while securing people, processes, and technology. This holistic approach is crucial in today's complex cybersecurity environment.
He gives back by producing a podcast, “Breaking into Cybersecurity,” focused on helping people transition into the cybersecurity industry by sharing the stories of those who have done it in the past five years to inspire those looking to do it now. He also co-authored “Develop Your Cybersecurity Career Path: How to Break into Cybersecurity at Any Level” and “Hack the Cybersecurity Interview: A Complete Interview Preparation Guide for Jumpstarting Your Cybersecurity Career”. He also hosts the 'Breaking into Cybersecurity' podcast, sharing stories to inspire those entering the field. Check it out here: https://feeds.captivate.fm/breaking-into-cybersecurity/ and video versions on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@BreakingIntoCybersecurity. My company also hosts a Substack - https://substack.cpf-coaching.com and podcast on Youtube - https://www.youtube.com/@cpfcoachingLLC
Christophe holds a Master of Science in Information Technology, Information Assurance, and Cybersecurity, a graduate certificate in Information Systems, and a bachelor's degree in Business Administration/Information Systems from Walden University. These include several industry certifications like the CISSP, GSLC, etc.
Available For: Advising, Authoring, Consulting, Influencing, Speaking
Travels From: Haymarket, VA
Speaking Topics: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Career Development, Business strategy, Social Media, Marketing
| Christophe Foulon | Points |
|---|---|
| Academic | 45 |
| Author | 1922 |
| Influencer | 405 |
| Speaker | 0 |
| Entrepreneur | 0 |
| Total | 2372 |
Points based upon Thinkers360 patent-pending algorithm.
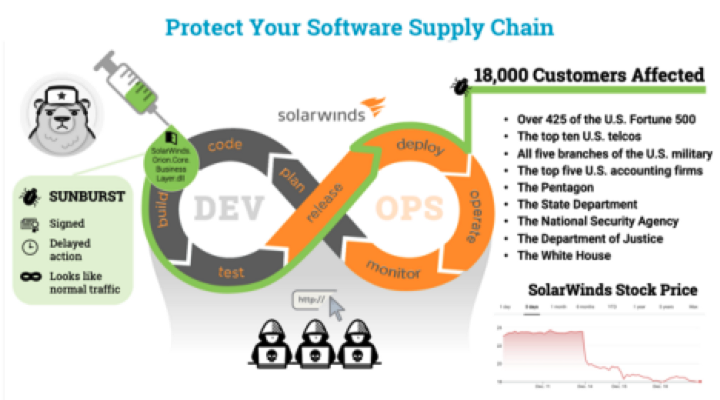 Understanding Your Digital Supply Chain Risk
Understanding Your Digital Supply Chain Risk
Tags: Cybersecurity, Risk Management, Supply Chain
 AI-Powered Phishing: The Top Threat for SMBs in 2025 – and How to Fight Back
AI-Powered Phishing: The Top Threat for SMBs in 2025 – and How to Fight Back
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Your 'Secure' Data Isn't Safe. Here's Why.
Your 'Secure' Data Isn't Safe. Here's Why.
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Strengthening Your Digital Defense: Practical Cybersecurity Approaches for SMB Tech Executives in 2025
Strengthening Your Digital Defense: Practical Cybersecurity Approaches for SMB Tech Executives in 2025
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Implementing Zero Trust Security for Small and Medium Businesses with Microsoft Solutions
Implementing Zero Trust Security for Small and Medium Businesses with Microsoft Solutions
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Review of the 2025 Verizon DBIR
Review of the 2025 Verizon DBIR
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
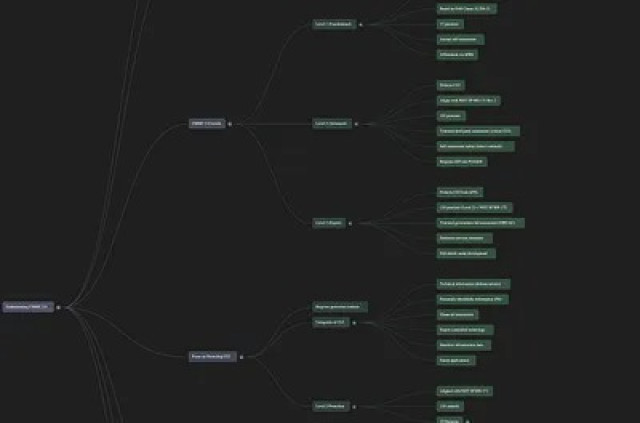 Navigating CMMC 2.0: A Strategic Imperative for Tech Leaders Protecting CUI
Navigating CMMC 2.0: A Strategic Imperative for Tech Leaders Protecting CUI
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
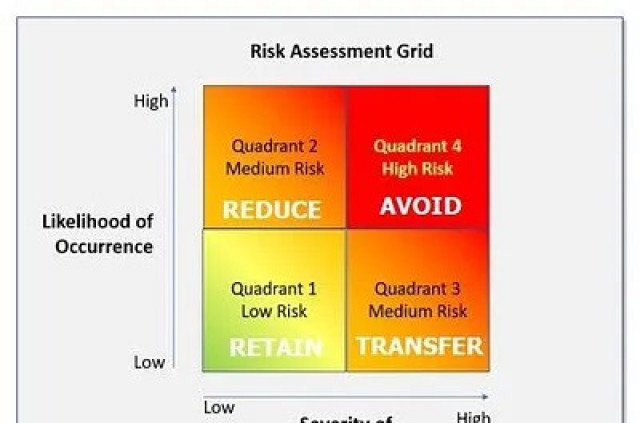 Crafting an Effective Overall Risk Management Plan for SMBs from Scratch
Crafting an Effective Overall Risk Management Plan for SMBs from Scratch
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
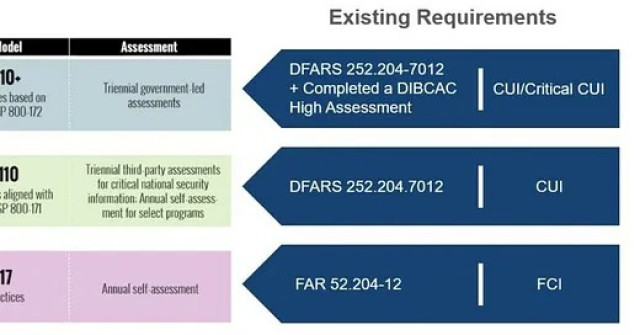 Navigating NIST 800-171 Compliance: A Strategic Guide for SMBs
Navigating NIST 800-171 Compliance: A Strategic Guide for SMBs
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Combating Security Platform Fatigue: A Strategic Approach to Tool Consolidation
Combating Security Platform Fatigue: A Strategic Approach to Tool Consolidation
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Building a Robust Data Governance Strategy for SMBs
Building a Robust Data Governance Strategy for SMBs
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Safely Implementing AI for SMBs
Safely Implementing AI for SMBs
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Associate, Community Recognition & Development at Thinkers360 | B2B Influencer Marketing
Associate, Community Recognition & Development at Thinkers360 | B2B Influencer Marketing
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Getting your SMB ready for AI use safely
Getting your SMB ready for AI use safely
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 AI-Powered Gamification: Revolutionizing Cybersecurity Training for SMBs
AI-Powered Gamification: Revolutionizing Cybersecurity Training for SMBs
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Proposed 2025 HIPAA Security Rule Changes & SMB Implications
Proposed 2025 HIPAA Security Rule Changes & SMB Implications
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Connecting DHCP Data Sources to Microsoft Sentinel, Querying with KQL, and Creating Custom Dashboards
Connecting DHCP Data Sources to Microsoft Sentinel, Querying with KQL, and Creating Custom Dashboards
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Stepping into Zero Trust with a Solid Strategy
Stepping into Zero Trust with a Solid Strategy
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Azure Security Best Practices for Small to Medium-Sized Businesses
Azure Security Best Practices for Small to Medium-Sized Businesses
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 The Identity and Data Management Challenge for SMBs: Navigating the Digital Landscape
The Identity and Data Management Challenge for SMBs: Navigating the Digital Landscape
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Preparing Your Data Governance Journey for AI
Preparing Your Data Governance Journey for AI
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Building Cybersecurity Culture: Engage Employees & Mitigate Risk
Building Cybersecurity Culture: Engage Employees & Mitigate Risk
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Essential Cybersecurity Policies for SMBs: A Blueprint for Protection and Growth
Essential Cybersecurity Policies for SMBs: A Blueprint for Protection and Growth
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Top 5 Cybersecurity Challenges for Small Businesses
Top 5 Cybersecurity Challenges for Small Businesses
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 The Importance of Data Security Posture Management for SMB Leaders
The Importance of Data Security Posture Management for SMB Leaders
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Mastering Cyber Incident Response for Small Businesses
Mastering Cyber Incident Response for Small Businesses
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Enhancing SMB Security: The Business Value of Hardening Guidelines in NIST CSF
Enhancing SMB Security: The Business Value of Hardening Guidelines in NIST CSF
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Maximize Business Security: The Critical Purpose and Value of DDoS Protection
Maximize Business Security: The Critical Purpose and Value of DDoS Protection
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Integrating Application Security into Your SDLC A Guide for Business Leaders
Integrating Application Security into Your SDLC A Guide for Business Leaders
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Integrating Application Security into Your SDLC A Guide for Business Leaders
Integrating Application Security into Your SDLC A Guide for Business Leaders
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 The Service Accounts Conundrum: What They Are and How to Secure Them
The Service Accounts Conundrum: What They Are and How to Secure Them
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Enhancing Business Strategies with Cybersecurity: Practical Steps for Businesses of All Sizes
Enhancing Business Strategies with Cybersecurity: Practical Steps for Businesses of All Sizes
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Hack the Cybersecurity Interview: A complete interview preparation guide for jumpstarting your cybersecurity career
Hack the Cybersecurity Interview: A complete interview preparation guide for jumpstarting your cybersecurity career
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Develop Your Cybersecurity Career Path: How to Break into Cybersecurity at Any Level
Develop Your Cybersecurity Career Path: How to Break into Cybersecurity at Any Level
Tags: Business Strategy, Cybersecurity, Entrepreneurship
 CPF Coaching Gumroad Affiliate program
CPF Coaching Gumroad Affiliate program
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Cybersecurity career advice from a cyborg
Cybersecurity career advice from a cyborg
Tags: Generative AI, Cybersecurity, Leadership
 Four Easy Steps for Achieving your Goals
Four Easy Steps for Achieving your Goals
Tags: Change Management, Leadership, Social
 Job Hunting Strategies: Advancing your career in cybersecurity
Job Hunting Strategies: Advancing your career in cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Advance your Career in Cybersecurity
Advance your Career in Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 The Top 10 LinkedIn Security Tips: Leaderboards are no longer just in the office
The Top 10 LinkedIn Security Tips: Leaderboards are no longer just in the office
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
 The practical components of a Cybersecurity Program
The practical components of a Cybersecurity Program
Tags: Cybersecurity, Digital Transformation, Leadership
 Developing your Security Program: Part 3
Developing your Security Program: Part 3
Tags: Cybersecurity, Digital Transformation, Leadership
Tags: Cybersecurity, Digital Transformation, Leadership
 Developing a Winning Marketing Strategy for your cybersecurity program
Developing a Winning Marketing Strategy for your cybersecurity program
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
 Developing your Security Program: Part 1 — Meeting the Stakeholders
Developing your Security Program: Part 1 — Meeting the Stakeholders
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
 How to Prioritize Workloads with Family Emergencies
How to Prioritize Workloads with Family Emergencies
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
 Develop Your Cybersecurity Career Path
Develop Your Cybersecurity Career Path
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
 AI in business decision making: Understanding the Risks and Potential Mitigations for AI-driven Decision-Making
AI in business decision making: Understanding the Risks and Potential Mitigations for AI-driven Decision-Making
Tags: AI, Business Strategy, Coaching
 Unlocking the Possibilities of AI for Businesses
Unlocking the Possibilities of AI for Businesses
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
 A Personal Board of Directors
A Personal Board of Directors
Tags: Cybersecurity, Leadership, Business Strategy
Tags: AI, Cybersecurity, Risk Management
Tags: Business Strategy, Cybersecurity, Leadership
 Advancing your Cybersecurity Career
Advancing your Cybersecurity Career
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Breaking into Cybersecurity Leadership
Breaking into Cybersecurity Leadership
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership

Tags: Cybersecurity

Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
Tags: Cybersecurity
 Enhancing Threat Detection in SMBs: A Guide to NIST CSF Detection Capabilities
Enhancing Threat Detection in SMBs: A Guide to NIST CSF Detection Capabilities
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Ep11 - Navigating Cybersecurity Risks: From Strategy to Implementation w/ Christophe Foulon
Ep11 - Navigating Cybersecurity Risks: From Strategy to Implementation w/ Christophe Foulon
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Maximize Business Security: The Critical Purpose and Value of DDoS Protection
Maximize Business Security: The Critical Purpose and Value of DDoS Protection
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
Tags: Cybersecurity
 The Framework Foundation of NIST CSF as Risk Management for CISO & Practitioners
The Framework Foundation of NIST CSF as Risk Management for CISO & Practitioners
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Friday Conversation: Cybersecurity Frameworks Explained CIS, NIST, MITRE & More
Friday Conversation: Cybersecurity Frameworks Explained CIS, NIST, MITRE & More
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 The Pillars of Zero Trust, Trust but Verify feat Chris Foulon & James Azar
The Pillars of Zero Trust, Trust but Verify feat Chris Foulon & James Azar
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Demystifying Cybersecurity Frameworks like CIS, NIST, MITRE & Operationalizing Controls
Demystifying Cybersecurity Frameworks like CIS, NIST, MITRE & Operationalizing Controls
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Mastering Shadow IT: Strategies for Integrating Unsanctioned Tech into Your Golden Road Develop
Mastering Shadow IT: Strategies for Integrating Unsanctioned Tech into Your Golden Road Develop
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
Tags: Cybersecurity, Coaching
Tags: Cybersecurity, Coaching
Tags: Cybersecurity, Coaching
 The Pillars of Zero Trust_ Assuming Breach feat Chris Foulon & James Azar
The Pillars of Zero Trust_ Assuming Breach feat Chris Foulon & James Azar
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
 Two CISOs Talking Cyber Podcast - Zero Trust Security: Least Privilege
Two CISOs Talking Cyber Podcast - Zero Trust Security: Least Privilege
Tags: Cybersecurity, Future of Work, Leadership
Date : February 17, 2023
Date : February 17, 2023
Date : February 17, 2023
Date : November 22, 2023
 Translating Phishing into real life
Translating Phishing into real life
It was the first day of a conference, and we all gathered together. It started like a prank, but I loved the idea. This is a security awareness lesson that simulates what a malicious link in an email that is attempting to fish an individual might be in real life.
The premise of the exercise is to start by having one individual wear the fish badge without notifying anyone else that this activity is happening. As they go about their day, if someone asks them about the fish badge, They have clicked on the fishing link, and it is now there to wear the badge. They need to share in their words what phishing is and how this stimulates that in real life, and now it’s their turn to go phishing. The exercise continues, and the subject walks around until someone else. Ask them about the fish before passing it on.
You can make it fun by capturing pictures of each person who was caught with the phishing alongside the person who was fishing them and creating a montage of it after the fact, as well as showing the lifecycle of how fishing links and similar threats act activities on average.
Video highlighting the results
https://youtube.com/shorts/XQ9xweyRcKk?si=BN6C_y-JJG4bUXlJ
Tags: Cybersecurity, IT Strategy, Open Innovation
 Don't let your security program implode
Don't let your security program implode
The idea of submarine impulsion reminds me of how some security program functions. It's like a parallel between the two, where everything seems to be running smoothly, and suddenly, it all implodes.
Imagine being inside a submarine, relying on a complex propulsion system to navigate through water. Like the security program, it involves various mechanical and computational components to ensure everything is running as it should.
At first, the submarine and the company's security program operate seamlessly, fulfilling our respective roles effectively. The submarine moves forward, propelled by its powerful propulsion system, while a security program must diligently monitor and protect the system from potential threats, maintaining its integrity and stability.
However, life isn't without its challenges. In the case of the submarine, a malfunction or catastrophic failure within its propulsion system can lead to an implosion. Similarly, unforeseen vulnerabilities, an overwhelming surge of threats, or an internal flaw can trigger a similar implosion-like event for a company's security program.
When an implosion occurs within the security program, its protective mechanisms collapse or become overwhelmed. You lose the ability to detect and respond to threats effectively, potentially leading to breaches or a breakdown of the entire security infrastructure. It's like a sudden collapse, exposing the system to attacks, data breaches, or unauthorized access, which could result in significant damage or compromise of sensitive information.
Such implosions can be caused by various factors—ever-evolving cyber threats, zero-day vulnerabilities, inadequate security measures, or internal errors within an application's programming. Sometimes, it's a cascading failure, where a single vulnerability or flaw triggers a chain reaction that compromises the entire security system.
To prevent these implosions, you need constant evaluation and improvement. Staying updated with emerging threats, patching vulnerabilities regularly, conducting security audits, and implementing robust protocols are all crucial steps. Additionally, a layered defense strategy, with multiple security measures and redundant systems, helps mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure.
Understanding the causes and consequences of implosions is vital. It reminds me of the importance of being proactive, continuously improving my defenses, and staying vigilant to maintain the integrity and security of the systems you protect. Just like a submarine must ensure its propulsion system is functioning optimally, you must ensure that your security measures are always at their best to protect against potential implosions.
#cyber #data #security #programming #event #strategy #infrastructure #resilience #faulttolerance
Tags: Business Continuity, Cybersecurity, Digital Transformation
 Developing cybersecurity leadership talent pipelines
Developing cybersecurity leadership talent pipelines
It’s very common in many industries but it seems cybersecurity leadership talent pipelines are not as well established.Developing leadership talent pipelines involves identifying and grooming potential leaders within an organization so that when a leadership position becomes vacant, there is a ready pool of internal candidates to choose from. Here are some steps to establish effective leadership talent pipelines:
Identify critical roles within the organization that require strong leadership skills
Define the competencies required for these roles
Assess existing talent in the organization to identify potential candidates who possess these competencies
Create development plans for individuals deemed to have leadership potential, with specific learning and training opportunities
Provide coaching, mentoring, and ongoing feedback to employees who are part of the leadership talent pipeline
Establish a succession planning process that outlines the steps for when a leadership position opens up
Finally, ensure transparency and communication around the leadership talent pipeline so that employees know there are opportunities for growth and advancement within the organization.Interested in reaching out for helping your organization to develop a better approach?
Tags: Business Strategy, Culture, Leadership
 AI in business decision making: Understanding the Risks and Potential Mitigations for AI-driven Decision-Making
AI in business decision making: Understanding the Risks and Potential Mitigations for AI-driven Decision-Making
With the recent arms race of AI (artificial intelligence) integrated systems, including chatbots and decision-making systems, let’s dive into how and why businesses might want to use AI systems. AI can bring advantages and disadvantages to business decision-making.

Pros:
Some cons can include the following:
A study by Rose and Resurgent (2021) found that businesses that successfully integrated AI into their decision-making processes tended to have a more data-driven culture, a clear understanding of the value of AI, and a commitment to addressing ethical and bias concerns. The study also found that businesses that adopted AI experienced increased efficiency, improved accuracy in decision-making, and a competitive advantage over their rivals. While using AI in decision-making can bring many benefits to businesses, it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks and address ethical and bias concerns.
Training AI
Artificial intelligent systems are trained using supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning techniques.
Supervised learning is the most common approach in which an AI algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset. The algorithm in AI obtains a set of inputs and their corresponding outputs, and the goal is to learn a mapping from inputs to results that can be used for prediction or classification tasks.
Unsupervised learning involves training an AI algorithm on an unlabeled dataset. The algorithm finds patterns and relationships within the data without direction or guidance. This approach is commonly used for clustering, dimensionality reduction, and anomaly detection.
Reinforcement learning involves training an AI algorithm by providing rewards and punishments based on its actions. The goal is to maximize the total compensation over time. This approach is used in game-playing, robotics, and autonomous decision-making applications.
AI oversight
Training AI systems, implementing oversight, and decision-making processes are critical to ensuring that AI systems are trustworthy and operate ethically. Businesses should adopt a multi-faceted approach that includes transparency, human-in-the-loop, bias mitigation, and regulatory compliance.
Providing oversight and decision-making in AI systems is a significant challenge. To address this, businesses can implement some strategies, including
A study by Zhao et al. (2021) found that integrating human decision-makers into AI systems can improve the transparency and accountability of the decision-making process. The study also found that human-in-the-loop approaches can help mitigate the risk of biased outcomes and increase the overall accuracy of AI systems.
Data and Privacy Concerns
Organizations have data privacy and security concerns when processing their information by an outside party, such as a cloud service provider. The risks associated with having sensitive information processed by a third-party provider include unauthorized access to the data, data breaches, data theft, and data loss.
To mitigate these risks, organizations can take the following steps:
AI Model Development
Part of the data and organizational security considerations revolve around the development of the AI model and the platform it runs on. Developing an AI model in-house versus using an AI model provided by an outside party both have pros and cons, and the decision between the two depends on an organization’s specific needs and circumstances. Here are some key pros and cons of each approach:
Pros of developing an AI model in-house:
Cons of developing an AI model in-house:
Pros of using an AI model provided by an outside party:
Cons of using an AI model provided by an outside party:
In conclusion, While using AI in decision-making can bring many benefits to businesses, it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks and address ethical and bias concerns. Training AI systems and implementing oversight and decision-making processes are critical to ensuring they are trustworthy and operate ethically. Businesses should adopt a multi-faceted oversight approach that includes transparency, human-in-the-loop, bias mitigation, and regulatory compliance. To protect intellectual property and company data, they should conduct due diligence, implement encryption, use secure communication protocols, negotiate contract terms, and regularly monitor and audit cloud service providers. Lastly, they should consider the implications of in-house vs. outside development and operations of their businesses’ decision-making systems.
Citations:
Tags: Cybersecurity, Digital Disruption, Leadership
Location: Virtual Fees: 400
Service Type: Service Offered
Location: Virtual Fees: 512
Service Type: Service Offered