Jan05

In January 2026, DeepSeek researchers published a landmark paper titled "mHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections," solving a "foundational instability" problem that had previously limited the depth and complexity of AI models. This breakthrough centers on the Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm, a piece of linear algebra from 1967, which DeepSeek repurposed to ensure that signals remain numerically stable even in stacks hundreds of layers deep. By bridging nearly sixty years of mathematical theory with cutting-edge GPU engineering, DeepSeek has unlocked a pathway for the next generation of reasoning-first AI.
Since 2015, the industry standard for neural networks has been Residual Connections (ResNet), which provides a "highway" for information to skip through layers unchanged, preventing signals from fading. In late 2024, researchers introduced Hyper-Connections (HC)—a "multi-lane" version of this highway that allowed for richer mixing and more flexible information routing.
The Failure: While Hyper-Connections increased a model's expressive power, they were notoriously unstable. Without constraints, signal "energy" could be amplified by over 3,000x as it passed through deep networks. This frequently resulted in "loss spikes" and "NaN" (Not a Number) errors, effectively killing the training process.
To "police" these highways, DeepSeek implemented the Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm. This 1967 procedure iteratively normalizes a matrix until it becomes doubly stochastic—meaning every row and every column sums exactly to 1.0.
By forcing the mixing behaviour of Hyper-Connections onto this mathematical manifold (known as the Birkhoff Polytope), DeepSeek achieved:
The mathematical core of this stability layer is derived from the following seminal work:
Sinkhorn, R., & Knopp, P. (1967). Concerning nonnegative matrices and doubly stochastic matrices. Pacific Journal of Mathematics, 21(2), 343-348.
In this paper, Sinkhorn and Knopp proved that any square matrix with strictly positive entries can be transformed into a doubly stochastic matrix by repeatedly scaling its rows and columns. While initially a problem of pure linear algebra, DeepSeek realized that this "Sinkhorn iteration" provides a perfect mechanism for Signal Normalization. By ensuring the mixing matrix $W$ satisfies $\sum_i W_{ij} = 1$ and $\sum_j W_{ij} = 1$, the network is prevented from adding artificial energy to the data stream, a requirement for training models with hundreds of layers.
The reason the Sinkhorn-Knopp iteration is so reliable for AI training is rooted in its mathematical proof of convergence. The proof essentially rests on the Total Support property.
This rigorous guarantee ensures that the "Manifold Constraint" in mHC isn't just a heuristic, but a mathematical certainty.
The Birkhoff Polytope is the set of all $n \times n$ doubly stochastic matrices. In the context of high-dimensional information, it functions as a geometric safe zone:
The stability provided by mHC enables the Internalized Chain of Thought (CoT). Traditionally, models perform reasoning by writing out steps in text. With mHC, researchers can stack hundreds of layers that act as internal reasoning modules. Because the signal remains stable, the model can perform multiple "logical passes" on information within its own internal layers before generating an answer.
Normalizing matrices thousands of times per second is typically too slow for industrial AI training. DeepSeek solved this through rigorous infrastructure optimization:
Industry analysts view the mHC paper as a technical preview for the rumoured DeepSeek-R2 flagship model, expected to launch around the Spring Festival in February 2026. DeepSeek-R2 was initially expected in 2025 but faced delays due to performance dissatisfaction and chip shortages. By implementing mHC, DeepSeek is expected to:
DeepSeek didn't just find a "patch"; they found a way to build a more complex "brain" that is mathematically guaranteed not to lose its mind during training. Looking back to 1967, they provided the structural integrity needed for the AI of 2026 to think more deeply, remain stable, and push the boundaries of machine reasoning.
This breakthrough provides a visual breakdown of how the Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm acts as a safety rail, preventing signal explosion in the deep neural networks of the future. This DeepSeek mHC architecture explanation provides a high-level visual summary of how these mathematical manifolds facilitate smooth information flow across complex neural pathways.
The application of 1967 mathematics to the AI landscape of 2026 represents a profound turning point in the quest for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). By reaching back to the Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm, researchers have effectively solved the "structural fragility" that once capped the intellectual growth of neural networks.
This synthesis of mid-century linear algebra and modern GPU engineering has done more than stabilize training; it has granted models a "permanent internal logic". In 2026, the path to AGI is no longer just about adding more data or more power; it is about the mathematical elegance of equilibrium. The Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm has become the stabilizer for a new era of "Internalized Reasoning," proving that the blueprints for our most advanced future minds were already written decades ago in the pages of pure mathematics.
Implementation Resources:
The complete Python implementation of the execution logic for both PyTorch and JAX, projecting matrices onto the Birkhoff Polytope manifold as detailed in this research, is available on GitHub.
This visual explanation of DeepSeek's mHC architecture summarizes how these mathematical manifolds facilitate deeper "thinking streams" in modern Transformers.
Keywords: Agentic AI, AGI, Generative AI
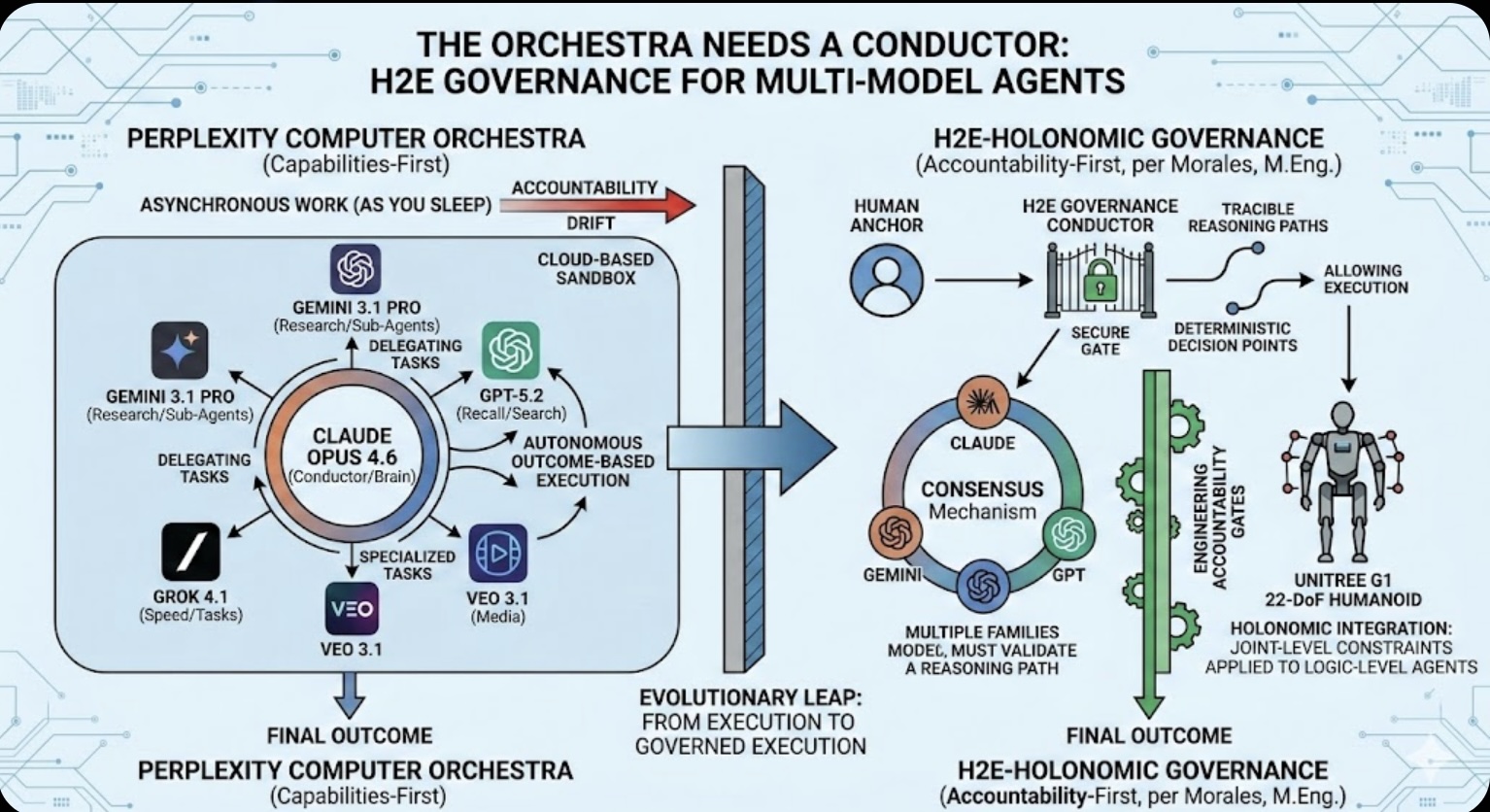 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business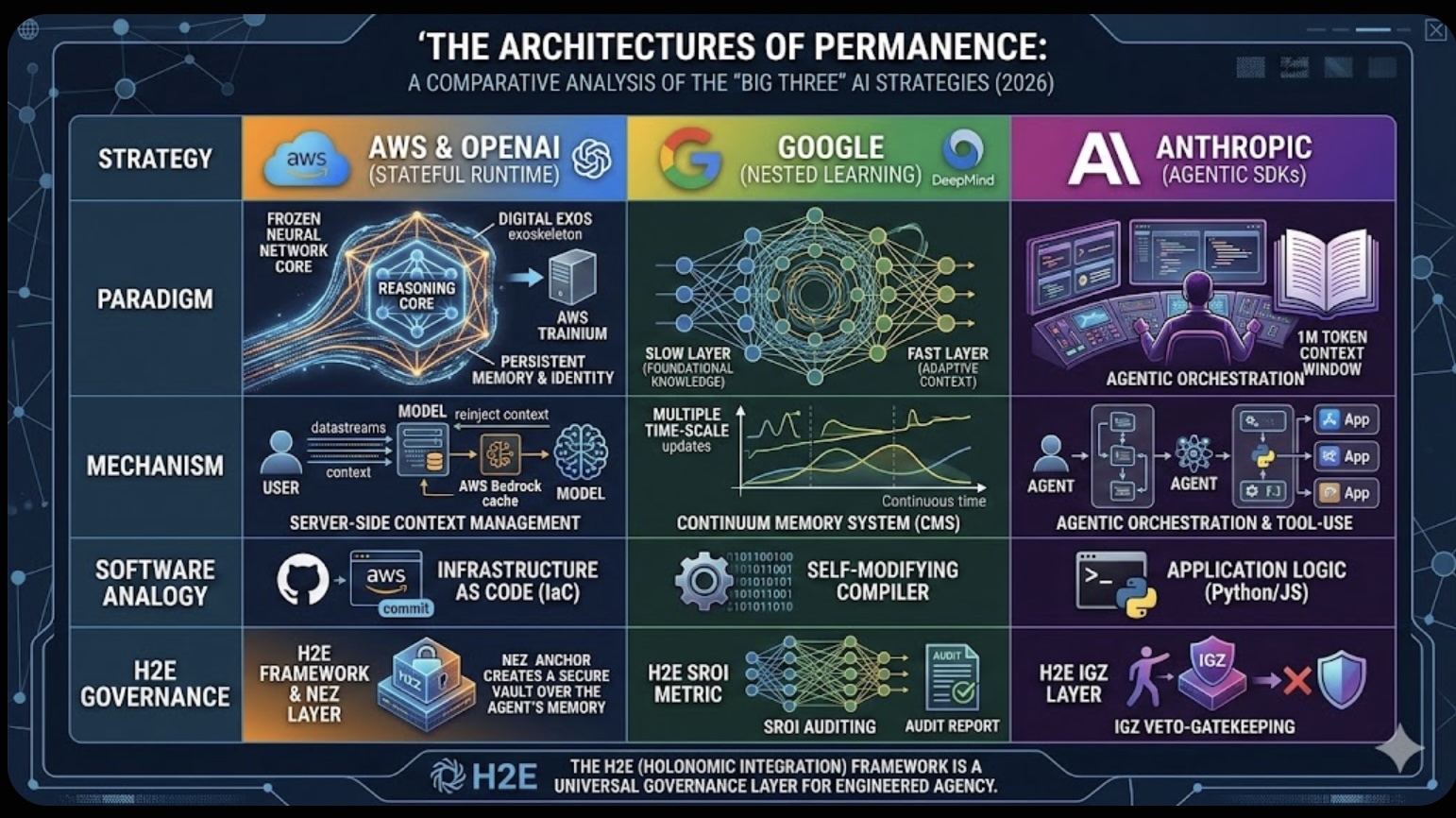 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026