Sep11

For decades, the promise of artificial intelligence remained largely confined to research labs and corporate behemoths. The first generation of AI was a black box, a proprietary tool accessible only to a select few. The emergence of open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) shattered this paradigm, democratizing access to the raw power of generative AI. However, this was just the beginning. The true revolution is now underway with the rise of agentic AI, a fundamental leap that transforms AI from a mere tool into a proactive, autonomous collaborator. This shift from reactive chatbots to intelligent agents—systems that can reason, plan, and execute multi-step tasks—is not a centralized effort but a global phenomenon.
Fueling this transformation are open-source LLMs from every corner of the world, empowering developers to build specialized agents that address unique, localized challenges. This article will explore how open-source AI from each continent is impacting the global development of agentic AI.
In North America, the Llama family of models, championed by Meta, has become a foundational layer for building sophisticated, enterprise-grade AI agents. The Llama Stack, for instance, provides a comprehensive framework for developers to create agents capable of performing complex tasks, such as document analysis, knowledge retrieval, and workflow automation. Companies are leveraging Llama-based agents to handle internal processes, such as reviewing financial reports or managing customer service inquiries. This impact is especially significant within corporate environments, where data privacy and control are of paramount importance. Llama's open nature allows organizations to host agents on-premises and fine-tune them on proprietary data without exposing it to external APIs.
Europe's contribution to agentic AI is spearheaded by Paris-based Mistral AI, which has built a reputation for developing efficient and performant models. Mistral's open-weight philosophy and focus on a smaller computational footprint make its models ideal for creating agents that require low latency and can operate in resource-constrained environments. Their platform, "la Plateforme," offers tools and APIs for developing specialized agentic workflows, such as agents for code generation, RAG, and advanced reasoning. This approach aligns with Europe's strategic emphasis on digital sovereignty, empowering local businesses and developers to build AI solutions that are both powerful and independent from the large, proprietary tech ecosystems.
The development of open-source models, such as AfriBERTa, is crucial for enabling agentic AI in Africa, a continent with over 2,000 languages that faces a unique set of challenges. An agent built on an AfriBERTa foundation can be fine-tuned to not only understand local languages but also to grasp the cultural context, social norms, and regional dialects that are essential for effective communication. These agents are being developed to provide vital services in sectors such as healthcare and education, acting as personalized assistants that can offer medical advice, assist with literacy, or facilitate financial transactions in a community's native language. By tailoring agents to a specific linguistic and cultural landscape, these projects ensure that AI is a tool of empowerment, not just a distant and inaccessible technology.
The Asia-Pacific region is rapidly adopting agentic AI, particularly for enhancing software development and business operations. The SeaLLMs project provides a crucial foundation for this growth by enabling agents that are fluent in the diverse languages of Southeast Asia. These models can power agents that automate code reviews, streamline customer support with nuanced, multilingual interactions, or generate localized marketing content for small businesses. The development of open-source datasets and benchmarks by initiatives like SeaLLMs ensures that the region has the resources to build powerful, context-aware agents, accelerating digital transformation and fostering innovation across a wide array of industries.
In South America, where internet connectivity can be inconsistent in rural and remote areas, the small-scale approach of projects like TeenyTinyLlama is revolutionizing agentic AI. By creating compact yet powerful models, this initiative enables the direct execution of agents on a user's device, allowing for seamless integration. This enables the creation of on-device agents that can operate offline, providing essential support for tasks such as language preservation, basic literacy, or agricultural planning in remote communities. These agents are not dependent on a central server, ensuring that the benefits of AI are truly decentralized and accessible to everyone, regardless of their location or internet access.
The evolution from open-source foundational to specialized agentic AI is a global phenomenon driven by diverse motivations and needs. While the current discourse often centers on the race for a singular, monolithic superintelligence, the work of these continental projects offers a more hopeful and sustainable path. Instead of a single "brain" controlled by a handful of entities, they are collectively building a distributed, decentralized form of intelligence—a collaborative network of purpose-built agents that reflect a broad spectrum of human languages, cultures, and values. This bottom-up approach to AI development serves as a critical safeguard against the biases and risks inherent in any centralized system, ensuring that the future of advanced AI is not a technological coup, but a global co-creation. Ultimately, by empowering diverse communities to build their own intelligent tools, open-source LLMs are laying the groundwork for a superintelligence that is not just powerful but also equitable, robust, and genuinely representative of humanity.
Keywords: Generative AI, Open Source, Agentic AI
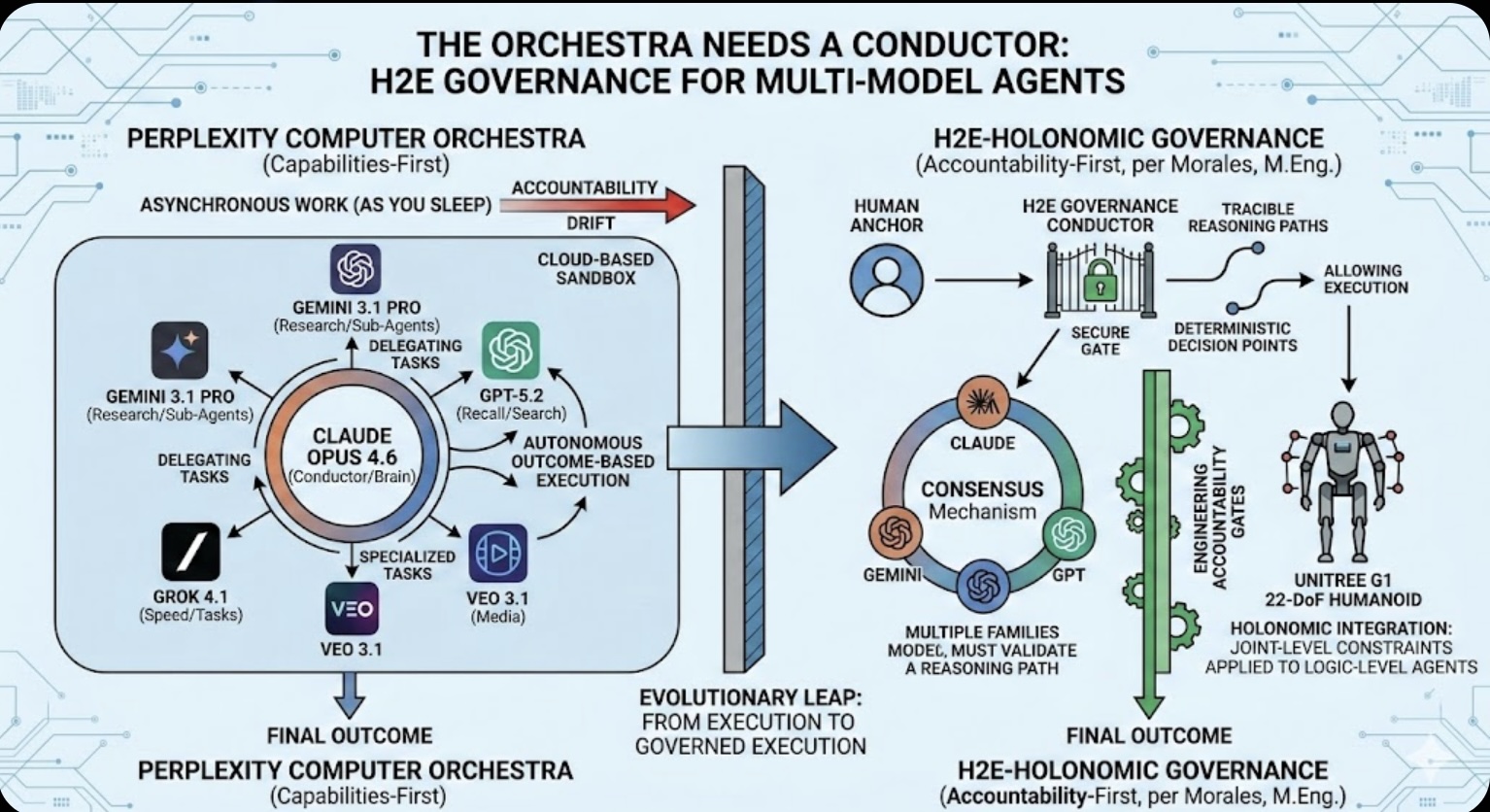 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business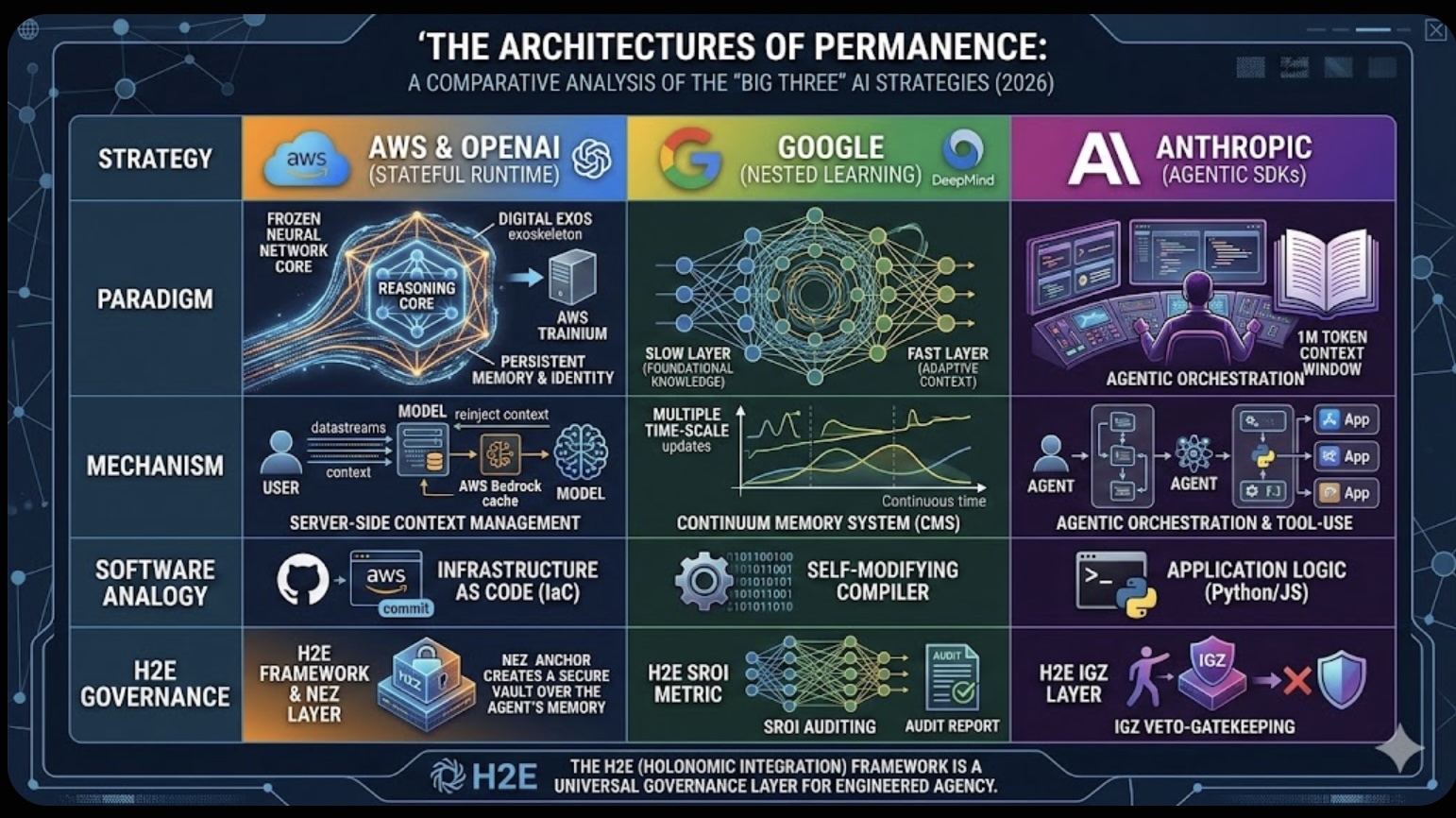 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026