Oct06

Operational risk is one of the most significant exposures boards and executives face. It can halt service delivery, erode trust, and trigger regulatory attention. Yet it also provides one of the strongest opportunities to strengthen governance and build resilience.
The Operational Risk Management Framework: Identify, Mitigate & Monitor article shows how leading organisations turn operational risk into foresight. It highlights the importance of ownership, culture, and capacity as the foundations of a mature operational risk environment. When these elements are aligned, risk management becomes a source of confidence and strategic advantage.
Operational risk management works best when it is integrated into daily decision-making. High-performing organisations align governance, culture, and capacity to ensure that ownership is visible and escalation is timely.
This approach transforms operational risk into a leadership discipline that supports execution and strengthens organisational trust. Clarity of accountability, simplicity of control, and open dialogue create the conditions for foresight and adaptability.
Industry data continues to show why this shift matters.
The next stage of maturity will depend on how effectively organisations translate these insights into real-time monitoring, decision support, and accountability loops.
Executives can embed operational risk as a strategic discipline by focusing on three priorities.
Clarify Ownership and Accountability: Assign ownership at the right level and define clear escalation pathways. Accountability must be visible and reinforced through leadership behaviour.
Simplify Controls and Processes: Streamline control frameworks and remove duplication. A focused control environment directs assurance where it adds the most value and improves engagement across teams.
Strengthen Culture and Behaviour: Operational resilience depends on how people act. Leadership tone, trust, and psychological safety ensure that weak signals are raised early and decisions reflect reality.
Boards are increasingly expected to demonstrate that operational risk frameworks work in practice. Effective oversight means understanding how ownership, culture, and capacity interact.
Boards that link operational risk to risk appetite, tolerance, and capacity create alignment between ambition and resilience. They gain visibility on how the organisation performs under stress and can act before limits are tested.
Technology and data now shape how operational risk is managed. Integrated dashboards, AI-assisted monitoring, and automated control testing give leaders a real-time view of resilience and capacity. These tools turn operational data into insight and foresight.
When technology supports ownership and behaviour, it enhances the quality of decisions and reinforces governance credibility.
Operational risk management is a continuous discipline that reflects how organisations lead and learn. Its strength lies in clear ownership, consistent behaviour, and data that supports timely decisions.
When boards and executives integrate strategy, governance, and culture, operational risk becomes more than a safeguard. It becomes a capability that protects value, strengthens resilience, and builds lasting trust.
By Julien Haye
Keywords: Culture, Risk Management, GRC
 Lateral Moves: The Most Overlooked Succession Strategy in Companies
Lateral Moves: The Most Overlooked Succession Strategy in Companies The Asset Play: Timing, Structure & Global Arbitrage
The Asset Play: Timing, Structure & Global Arbitrage 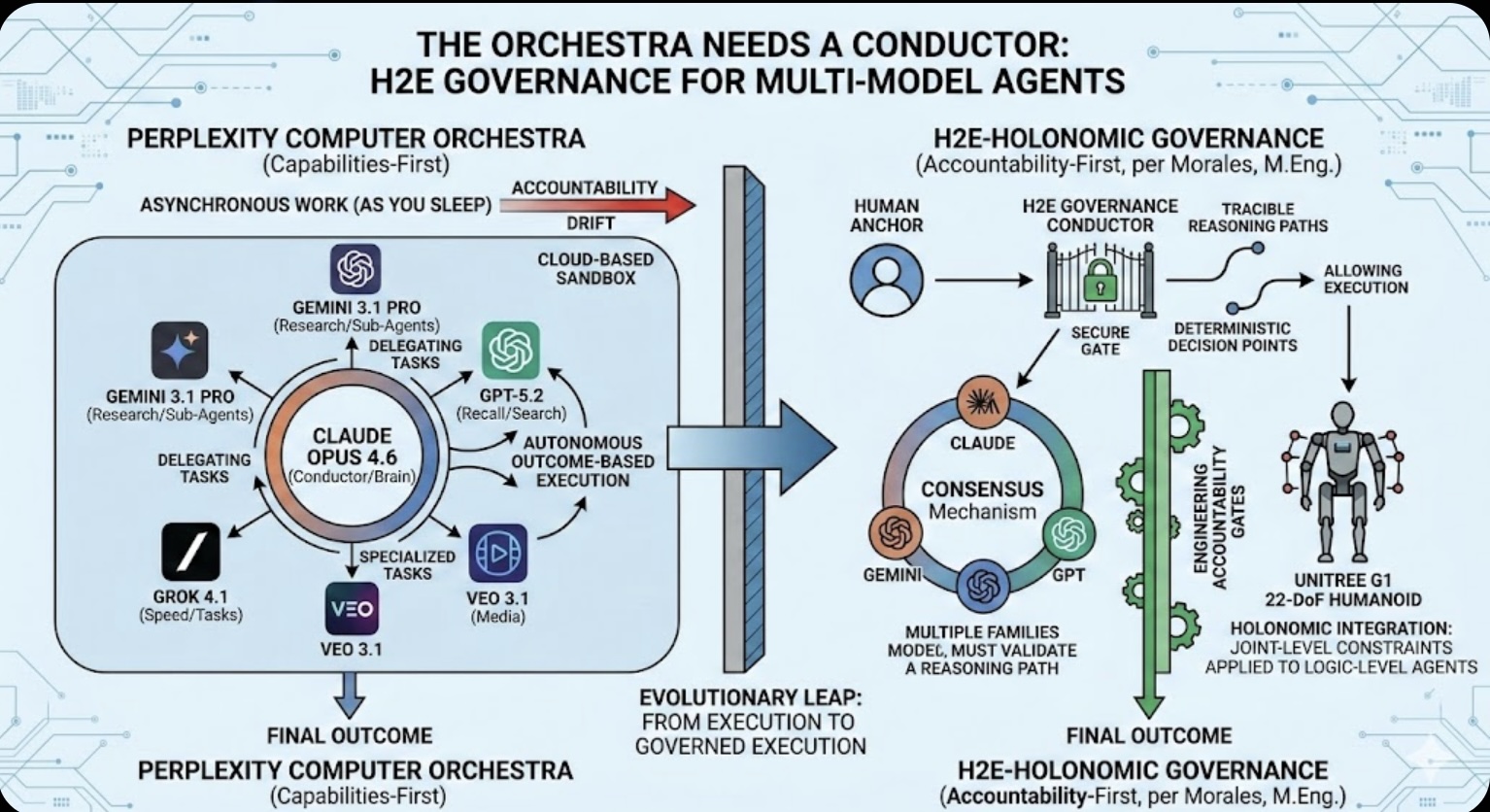 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business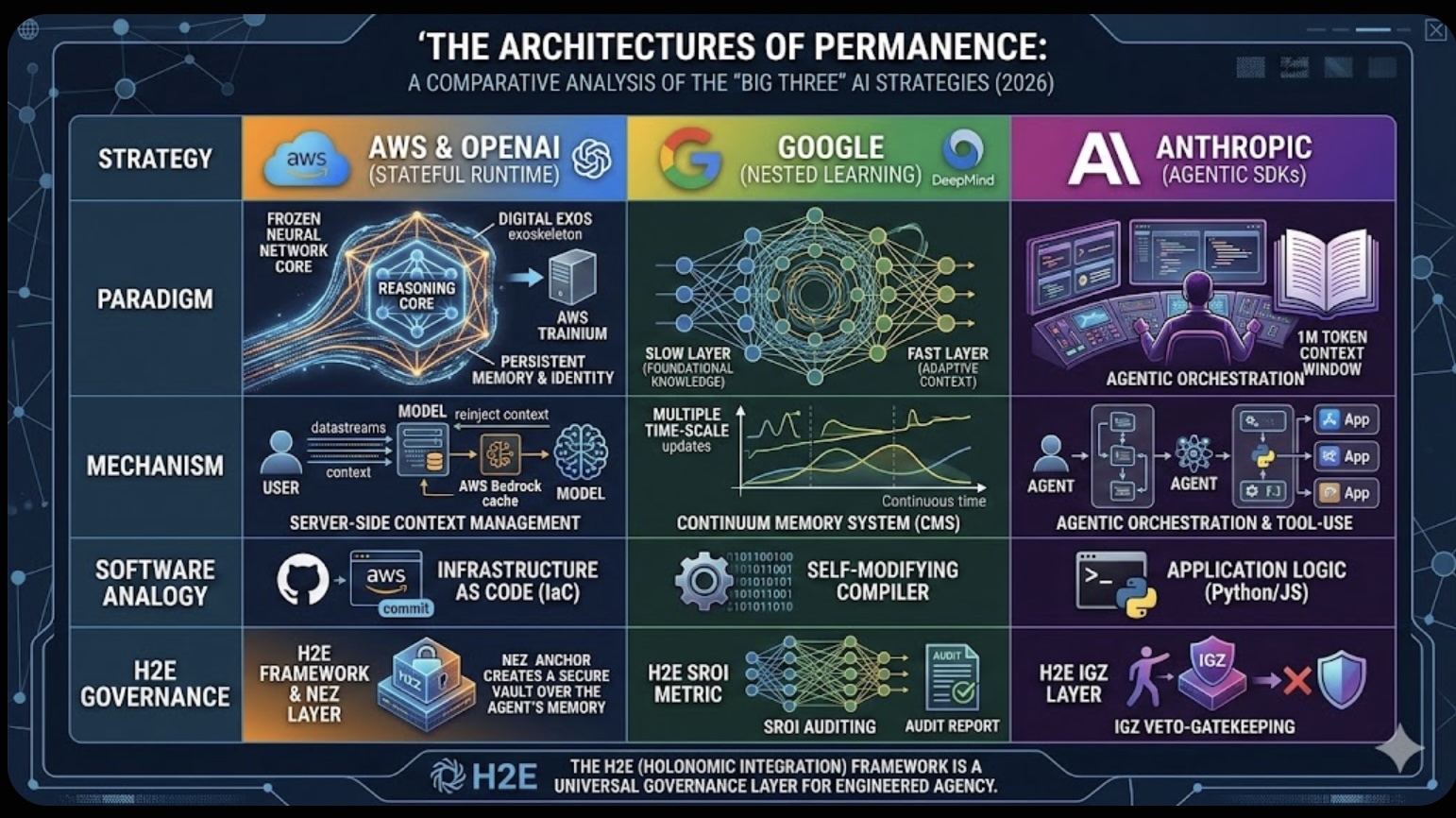 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)