 TOEFL
TOEFL
TOEFL
February 25, 2024
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
robotic coding
international Dublin University phD
February 17, 2024
Section 7: Design with 3D Printers and Tinkercad
In today's technology, turning many designs from dream to reality; both software
support and new generation devices, getting rid of high costs and providing a lower cost
can be realized. 3D Printers have provided the biggest development in this regard. Software such as Tinkercad, which can be learned more easily instead of special drawings, has been developed to enable end users to design.
7.1. Three Dimensional Printers
A 3D printer is a machine that converts software-designed 3D objects into solid form. In 2006, thanks to the Reprap (do-it-yourself project), many ordinary users started using these devices as hobbyists.
The advantages of 3D printers are as follows.
- The design can be shared and improved as it is produced in virtual environments.
- Changes and corrections can be made quickly.
- Personalized products can be easily produced.
- Efficient in terms of investment and production.
- Relatively low initial investment cost.
- Product price can be calculated before production.
- Use of recyclable materials.
- Minimal material waste.
Many technologies are used to create 3D products. The differences between technologies are often related to how the layers are formed. For example, there are many models such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Poly Jet Modeling (Additive Manufacturing - Addi-tive Modeling), Selective Laser Sintering SLS (Selective Laser sintering).
7.2. Modeling for Three Dimensional Printers: Tinkercad
In Section 3.2, how to register in Tinkercad is explained in the simulation section.
In panel 1; the name of the project is determined.
Panel 2; Copy, Paste the object added to the scene in the project. Delete. There is a section with Undo and Forward buttons.
In panel 3; there are buttons to display the front, side and back views of the objects added to the scene, square, Main Screen view, Focus on selected objects, Zoom in, Zoom out, Flat view can be edited.
Area number 4; the work area where objects can be added.
Panel 5 has Group Objects, Ungroup, Align and Mirror Options.
In area 6, there are options to import, export and send project files.
In panel 7, there are Design, Blocks, Brick as view. Next to the View menu, there is a button to invite others to work and settings related to personal account.
In panel 8; there is an area where objects can be added.
In panel 9; the dimensions of the grid panel and grid operation settings can be made.
7.2.1. Creating an Application with Tinkercad
In Tinkerkad works, objects are added and removed from the workspace. An example of this is seen in Figure 7.7 as adding a box.
By adding the hole version of the Hole Cylinder object in Figure 7.15 to the project, a gap (cut) can be made on the other object.
As shown in Figure 7.16, Solid Box and Hole Cylinder can be combined inside each other to give shape to the objects. In this area, the junction areas of the solid object and the hole object can be organized by combining and grouping the box object and the hole object as desired.
The Group menu is used to combine two objects. This tool can be used for merging or subtracting objects. By selecting the two objects in Figure 7.16 and clicking Group in Figure 7.17, the two objects are now merged into one object. By merging in this area, a space object is subtracted from a box object.
Section 7: Design with 3D Printers and Tinkercad
In today's technology, turning many designs from dream to reality; both software
support and new generation devices, getting rid of high costs and providing a lower cost
can be realized. 3D Printers have provided the biggest development in this regard. Software such as Tinkercad, which can be learned more easily instead of special drawings, has been developed to enable end users to design.
7.1. Three Dimensional Printers
A 3D printer is a machine that converts software-designed 3D objects into solid form. In 2006, thanks to the Reprap (do-it-yourself project), many ordinary users started using these devices as hobbyists.
The advantages of 3D printers are as follows.
- The design can be shared and improved as it is produced in virtual environments.
- Changes and corrections can be made quickly.
- Personalized products can be easily produced.
- Efficient in terms of investment and production.
- Relatively low initial investment cost.
- Product price can be calculated before production.
- Use of recyclable materials.
- Minimal material waste.
Many technologies are used to create 3D products. The differences between technologies are often related to how the layers are formed. For example, there are many models such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Poly Jet Modeling (Additive Manufacturing - Addi-tive Modeling), Selective Laser Sintering SLS (Selective Laser sintering).
7.2. Modeling for Three Dimensional Printers: Tinkercad
In Section 3.2, how to register in Tinkercad is explained in the simulation section.
In panel 1; the name of the project is determined.
Panel 2; Copy, Paste the object added to the scene in the project. Delete. There is a section with Undo and Forward buttons.
In panel 3; there are buttons to display the front, side and back views of the objects added to the scene, square, Main Screen view, Focus on selected objects, Zoom in, Zoom out, Flat view can be edited.
Area number 4; the work area where objects can be added.
Panel 5 has Group Objects, Ungroup, Align and Mirror Options.
In area 6, there are options to import, export and send project files.
In panel 7, there are Design, Blocks, Brick as view. Next to the View menu, there is a button to invite others to work and settings related to personal account.
In panel 8; there is an area where objects can be added.
In panel 9; the dimensions of the grid panel and grid operation settings can be made.
7.2.1. Creating an Application with Tinkercad
In Tinkerkad works, objects are added and removed from the workspace. An example of this is seen in Figure 7.7 as adding a box.
By adding the hole version of the Hole Cylinder object in Figure 7.15 to the project, a gap (cut) can be made on the other object.
As shown in Figure 7.16, Solid Box and Hole Cylinder can be combined inside each other to give shape to the objects. In this area, the junction areas of the solid object and the hole object can be organized by combining and grouping the box object and the hole object as desired.
The Group menu is used to combine two objects. This tool can be used for merging or subtracting objects. By selecting the two objects in Figure 7.16 and clicking Group in Figure 7.17, the two objects are now merged into one object. By merging in this area, a space object is subtracted from a box object.
The object shown in Figure 7.18 is the new Solid object after grouping the solid and the hole object.
Figure 7.19 shows the new objects resulting from grouping Box and Cylinder objects with different combinations in Tinkercad software application. The combinations of the objects are written under the newly formed objects.
After selecting the grouped objects, they can be restored with the Ungroup option.
Many combinations of solid and hollow objects can be used to draw a chess piece. Original products can be created by thinking creatively with these objects in different shapes. In Figure 7.21, the chess piece on the left was drawn using objects such as the many round cylinders on the right.
To draw a simple house, a box needs to be added. Add a box object to an empty scene and enter its horizontal and vertical dimensions of 60 mm. Its height is also set to 60 mm.
Drag the roof object from the Basic Objects onto the stage and set its dimensions to 60 mm horizontally and vertically and its height to 30 mm.
The reason for making the roof object 60 mm horizontally and vertically is that the dimensions given in the box are smaller than the dimensions given in the box.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 Globalization
Globalization
Mines Paris TEch University
April 12, 2023
5 Pillars of Globalization
See publication
Tags: Agile, Change Management, Sustainability
 Industry effects on city logistic
Industry effects on city logistic
Paris Tech University
April 13, 2022
City Logistics
Abstract
The world and industry are changing day by day. We just started industry 1.0 since 1712 and then system has been changing from the time. Especially the development of the industry 2000s sworn to increase and logistics must to entegre and develop same time. The Industrial development effects to city logistic directly and this development changing some process that city logistic has made it necessary to develop.
The industry established city center due to population then the most logistics activities switch to center but has been occur some problem. We must to think about;
How industry 4.0 will affect city logistics?
Developments in Industry 4.0 seriously affected city logistics, leading to the birth of city logistics 4.0; In this way, as well as improving different aspects of logistics such as sustainability, efficiency, ability to respond to customers and better traceability, the essential elements of the business have become affected from this. It is essential to analyze the impact of industry 4.0 on city logistics as a whole, since it is very important to establish a good cooperation between suppliers, manufacturers and customers in order to increase transparency in all steps from the moment the order is placed to the end of the product life.
The rapid development and integrated systems of industry 4.0 negatively affect city logistics. Because undeveloped infrastructures, population crowd, increasing volume of B2B negatively affected city logistics and made its development compulsory. Some negative effects;
• Infrastructure not meeting the need
• Length of the process
• Cost investment requirement
• Traditionalist approaches
• Technology integration issues
• Hackers and security threats
• Air pollution
• Water pollution
• Wastes
• Noise
• Area Usage
• Transportation Service Costs
• Traffic accidents
• Traffic Congestion
We needed to think about to problems to go solution. So the development of industrial systems could not be met by inadequate systems in city logistics. Non-integrated city logistics traditionally continued, causing complexity in cities. In order to meet the developments in industry, mass production, integrated systems, interaction with suppliers, mechanization and reduced human
impact, city logistics had to develop at the same pace.So the this development had bring many cost to city logictics if catch the industry 4.0.
The main reason for these problems is the continuous development of R&D, but the inability of urban logistics to develop at the same rate.
In cities where social, cultural, industrial and commercial activities take place together; increasing the quality of life, sustainable economic growth, logistics of goods produced and consumed in the city effective solutions can be provided by reducing negative effects on costs, increasing urban competitiveness and controlling environmental impacts such as energy consumption, visual pollution and noise pollution.
Some ways to minimize the negative impact of industrial development on city logistics:
• Applying Proper Rotation in Load Zones
• Deliveries at Night Time
• Classification of Roads
• Online Reservation Application for Loading Zones
• Using Advanced Traffic Management Systems
• Using cameras-CCTV (close-circuit tv cameras)
Some economical solutions
• Establishing Urban Logistics Forums
• Providing Information Support
• Integration of systems used in industry with systems used in city logistics
• Use of Advanced Vehicle Control and Safety 90 Systems
• Using cameras-CCTV (close-circuit tv cameras)
Those means the city lojistik generally must going solution on additive manufacturing,robotings and automation, cloud computing, Internet of Things and Internet of Services, Driverless Vehicles, Self-Learning Systems, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles.
In conclusion, city logistics has become more and more important in recent years due to the development of the industry in cities. The development of the industry causes many differences, problems and changes in urban logistics activities.
The main reason for these problems is the continuous development of R&D, but the inability of urban logistics to develop at the same rate.
It is obvious that city logistics should develop at the same pace with the industry and problems can be solved with some solutions.
References,
1. Allen, J., Tanner, G., Browne, M., Anderson, S., Christodolou ve G., Jones, P. (2003). Modelling policy measures and company initiatives for sustainable urban distribution. Final Technical Report, University Of Westminster,
2. Ballou, R.H. (1992). Business Logistics Management: Planning, Organizing and Controlling the Supply Chain. Fourth Edition, New Jersey:Prentice Hall
3. Szołtysek J. (2005): Logistyczne aspekty zarządzania przepływami osób i ładunków w miastach. Wydawnictwo Akademii Ekonomicznej, Katowice.
4. İnaç, H. ve Tanyaş, M. (2012). İstanbul’un Kentsel Lojistik Analizi ve Çözüm Önerilerinin AHP ile Değerlendirilmesi. 1.Ulusal Lojistik ve Tedarik Zinciri Kongresi Bildiri Kitabı (ss.137-147). Necmettin Erbakan Üniversitesi, Konya, 10-12 Mayıs 2012
5. Horenberg, Daan. “Applications With in Logistics 4.0 A Research Conducted on the Visions of 3PL Service Providers”. Thesis, University of Twente. 2017.
6. Stock Tim ve Guenther Seliger. “Opportunities of Sustainable Manufacturing in Industry 4.0”. Procedia CIRP. 40 (2016):536-541.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Role of AI in Enhancing Daily Work Life
The Role of AI in Enhancing Daily Work Life
Medium Article
February 22, 2024
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 GAP Nedir?
GAP Nedir?
Medium Gap
February 18, 2024
Gap Nedir?
İş hayatında "gap" (boşluk, açık), mevcut durum ile hedeflenen veya ideal durum arasındaki farkı ifade eder. Genellikle performans yönetimi, proje yönetimi, pazar analizi ve stratejik planlama bağlamında kullanılır. Özünde, bir gap analizi, bir organizasyonun veya bireyin şu anki konumu ile ulaşmak istediği hedefler veya standartlar arasındaki farkı belirlemek için yapılan bir çalışmadır. Bu analiz, eksikliklerin ve iyileştirme gerektiren alanların tespit edilmesine yardımcı olur ve bu boşlukların nasıl kapatılacağına dair stratejiler geliştirmek için bir temel sağlar.
Gap Analizinin Temel Bileşenleri
Mevcut Durumun Değerlendirilmesi: Organizasyonun veya projenin şu andaki durumu, performansı ve kaynakları detaylı bir şekilde incelenir.
2. Hedeflenen veya İdeal Durum: Organizasyonun veya projenin ulaşmayı hedeflediği durum, performans seviyesi veya hedefler belirlenir.
3. Boşlukların Tespiti: Mevcut durum ile hedeflenen durum arasındaki farklar (gap'ler) analiz edilir ve belirlenir.
4. Eylem Planının Oluşturulması: Tespit edilen boşlukları kapatmak için gerekli adımlar, stratejiler ve kaynaklar planlanır.
Gap Analizinin Önemi
Stratejik Planlama: Gap analizi, organizasyonların stratejik planlarını daha etkili bir şekilde oluşturmalarına ve uygulamalarına yardımcı olur.
Performans İyileştirme: Mevcut performans ile hedeflenen performans arasındaki farkları belirleyerek, iyileştirme alanlarını net bir şekilde ortaya koyar.
Kaynakların Etkin Kullanımı: Kaynakların, en çok ihtiyaç duyulan ve etki yaratacak alanlara yönlendirilmesini sağlar.
Risk Yönetimi: Potansiyel engeller ve zorluklar önceden tespit edilerek, risk yönetimi stratejileri geliştirilebilir.
Gap analizi, iş dünyasında karar verme süreçlerini destekleyen ve organizasyonların sürekli gelişim yolculuğunda önemli bir araç olarak hizmet eden stratejik bir yönetim aracıdır.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 encryption techniques
encryption techniques
dublin university old
February 17, 2024
1 ENTRANCE
In communication between individuals or institutions, there may be information that must be kept confidential. Privacy in communication has been an important issue since ancient times, especially in the military field. has happened. message hidden keeping about your day provided by technical to the possibilities according to Methods to ensure confidentiality have been researched and used.
It is known that in ancient Egypt, texts were encrypted with Egyptian hieroglyphic writing. Another known hiding method; It means shaving the messenger's head, writing the message on his head, and sending it to the other party after his hair grows. Another method is to write the message on a ribbon wrapped around a stick of a certain diameter; It is to fill the empty spaces on the ribbon with meaningless letters and simply send the ribbon to the other party. Another known encryption method used before modern encryption methods is the "Caesar Cipher" . In the following section, some encryption methods used in the past and today are explained:
1.1 encryption History
the history of encryption in three periods :
1. Machine either in Computer methods that do not use
2. Machine using methods
3. Computer methods using
Figure 1: Hieroglyph writing example
1.1.1 Machine either in Computer non-user Methods
It can be seen from historical documents that the documents to be hidden in Ancient Egypt were encrypted with different hieroglyphic methods. Hieroglyphic characters that ordinary people would not understand were used to hide messages.
Again, in Ancient Greece, a ribbon was wrapped around a cylindrical stick of a certain diameter. Then, the text to be conveyed is written in a line on the ribbon. Then, the ribbon is opened and meaningless letters are added to the empty spaces on the ribbon.
If the person receiving the ribbon has a stick of the same diameter, the text can be read.
In more recent times, encryption methods based on "substitution " have been used. This method is used in two ways.
Method- 1 ;
It is known as the first encryption algorithm known and widely used since the beginning of written history. The outline of this algorithm is as follows:
• One to the alphabet endures ( Phoenicia , Latin, Arabic alphabet etc. ).
• Instead of each letter, the text to be encrypted will contain letters n steps further in the alphabet. or replaces the letter behind it. The alphabet is thought of as a wheel After the letter, you go back to the beginning.
It is known that this method, also known as the “Caesar” algorithm, was applied in ancient times to documents written in the Hebrew alphabet, which was derived from the Arabic alphabet.
As can be understood from what has been explained, the basis of the Caesar Cipher algorithm is the number of letters at a certain distance rather than one letter. is to add another letter. In this method, the distance between the original letter kept secret and the letter replaced by it is the number n . An example of this method is shown in Figure-2.
Figure-2: Caesar encryption of the method of the foundation representation
Example; Caesar encryption For the algorithm ,
n : 3
Raw text: Arzu Cakmak Encrypted text : ofni qoyaoy
In this encryption algorithm, the number n is kept secret, and n is the message between the sender and the receiver. without being sent before decision given One is the number. This key buyer And transmitter between is kept secret .
The weakness of the Caesar encryption algorithm is; Explained with an example, instead of the letter 'a', 'o' If the letter is used and the letters are repeated, the equivalents of the letters can be found after a while.[2]
Method- 2;
By responding to the letters of the alphabet with unordered shapes, letters or numbers, the raw text is compared to these shapes, letters or numbers. Two examples of this method are shown in Figure-3.
A. B. C. C D TO F g Ğ I I H J. K
one 20 30 40 700 500 2 50 4 600 800 3 70 60
L. M. N HE HE P. R. S S T u Ü V Y Z. space
one thousand 50 200 300 80 400 8 6 9 7 10 900 5 90 one hundred 2000
Figure-3: In its place Do not put with encryption to the method related two example
Crude text: Desire to school Encrypted text to go:
181009002000300601010001508007005003050060
An application similar to the Ebced account was used in the Ottoman Empire. is considered.
This methods One machine either in computer non-user are techniques.
In its place Do not put of the method weak point One to the character opposite always same character is to produce.
n :1
Raw text: Ayşe Ali Encrypted text : Bztf bmh
Each two of the word encrypted of their state first of letters same is easily It can be said.
It is clear that it will be easy to decipher the encrypted text if it is known in which language the text was written. Considering that there were no computers at the time when these encryption methods were used; It can be said that a certain degree of confidentiality is maintained. It is clear that these algorithms were simple in the period when computers were used.
1.1.2 Machine User Methods
The most well-known encryption method performed using a tool is "Enigma" . enigma mechanical aspect made One It is an encryptor . your password was arranged Encryption is done with a machine consisting of 4 positioned wheels and a keypad. Figure-4 shows the Enigma encryption machine.
Figure-4: enigma encryption device [4]
The password is determined by positioning the gears, and then every text typed on the keypad is converted into encrypted text. “ Enigma ” was used by the German armed forces during World War II. Enigma's encryption method It is a known story that around 2000 scientists worked for two years to solve it and could not solve it. However, as a result of the capture of the Enigma device, all its secrets were revealed. The lesson learned from the Enigma encryption device is this: It is wrong to keep the encryption method secret; The correct thing is to hide the password. The openness of the encryption algorithm provides an opportunity to measure the robustness of the encryption method.
1.1.3 Computer User Methods
Computerized or non-computerized encryption methods are basically classified as symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods. The situation regarding symmetric encryption is shown in Figure-5. In this example, Ali and Ayşe want to hide their messages from others. This Therefore, your messages without encryption before, own between them One password They determine. More Then they send their messages to each other with this password. The encrypted text is decrypted with the same password. For this reason, it is called symmetric encryption.
Figure-5: Symmetrical encryption methods scenario
In the following period, encryption algorithms were developed as computer-aided encryption methods. The most well-known method developed in this period is DES ( Digital encription Standard), 3-way DES , AES ( Advaced encription Standard) is . This
encryption methods are known as symmetric encryption methods. The encryption method known as asymmetric is RSA . Details about these encryption methods will be given in the second part.
Encryption algorithms are not limited to encrypting only texts but can also be used to encrypt voice conversations. For example, the DES algorithm has the ability to encrypt sound. In order to encrypt a voice; The encryption algorithm must be fast enough to process audio. Since RSA is slower and software-based, it cannot be used for voice encryption.
One of the most important features of the DES algorithm is that it does not always produce the same character for each character.[5]
The DES encryption method uses a 64-bit block cipher . The ciphertext is generated with an encrypted 6-bit key. The least significant bit of each byte of the encrypted text is used as the parity bit. If the number of message bits is not divisible by 64; The last block is filled. Permutations and substitution methods are also included to make encryption even more difficult . First, by making a permutation on the 64-bit encrypted text ; 32 bit L i and R i It is divided into two parts in the form. The 16 bits chosen in the DES encryption method guarantee to eliminate the correlation between the encrypted text and the raw text. Figure-5 shows the outline of the DES encryption algorithm .
The DES algorithm was the most powerful algorithm known in the 1990s. However, with the increase in the speed and capabilities of computers, it has lost its unbreakability feature. For this purpose, the 3-way DES method started to be used. This encryption method applies the DES algorithm to the same text blocks 3 times. Therefore, it contains 3 DES keys. The keys may be different or the same. However, having different keys makes the encryption even stronger. Figure-6 shows the triple DES encryption algorithm.
Figure-6: DES encryption of the algorithm mother lines[ 6]
Figure-7: Triple DES encryption of the algorithm mother lines
There are many publications about these methods. A few of these are included in the bibliography .
RSA encryption Method
It is an asymmetric encryption method. There are two keys in this method. One of them is called a public key and the other is called a private key. A text encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted with the private key held by the person who produced that public key.[3]
An application where the RSA algorithm is widely used is internet banking. In this example, to the customer who connects to the bank with his public name (customer number), the bank issues its own public key. to the customer sends. customer's sent by each message This open with key is encrypted. Only the bank can decrypt the encrypted text.
AES encryption Method
As a result of the increase in the speed of computers, the decoding time of texts encrypted with the DES algorithm has shortened. For this reason, algorithms with higher encryption power were sought and AES was developed.
of android open source coded operating system to be and mobile to platforms APPLICATION
to develop wanting people for One ease to provide with also developed encryption The method was implemented as an Android application.
encryption algorithms only reusable password in production It is also used.
1.2 Thesis Scope
• Entrance In the section, of the subject general introduction made, encryption with relating to details given and methods that assist in the study are explained.
• Second in the part, of the project purpose, scope, risk management And timing place has received.
• Project Scope In the section, in the project used terms introduced And The proposed encryption method is explained step by step.
• Analysis And Modelling In the section, encryption of the method How It was announced that the key structure would be implemented and a detailed analysis of the key structure was made.
• Later, information about encryption with Android was given, interface images were included and its usage was explained.
• Next in the section If, encryption method about There are comments And Project outcomes are explained.
2 OF THE PROJECT DEFINITION AND PLAN
This section of the project all with relating to general study of knowledge Contains.
2.1 of the project Purpose
Our goal is to encrypt short texts (messages, messages) for a short time. Therefore, we accept that there is no need to develop a very strong encryption algorithm. Therefore with our algorithm programmed in case of A lot short And fast to happen We aim. The encryption algorithm is used not by experts , but in a way that non-experts cannot decipher. Such a goal would perform a very simple algorithm, demonstrating what simple encryption algorithms can do. With the widespread use of mobile phones, sending text messages via phones has entered our lives. via your mobile phone Sending encrypted text and voice without reporting the algorithm and password is also not desired by the public administration. The target determined within the scope of the thesis is not to develop a highly secure encryption algorithm to be used in encrypting military information.
2.2 of the project Scope
In the first part of the project scope, encryption methods were examined. For this purpose, firstly a source research was conducted. The superiority of existing encryption methods was evaluated and an algorithm that can be used on a mobile phone was created by us. The next stage is to write and test the logically designed encryption algorithm. The "text processor" required to write the message or text will be written by us. The messages prepared in this text processor will be transferred to the encryptor and the encrypted file will be sent to the recipient in an image format. On the side where the message is received, the decoding image It will parse the file and then pass it to the text viewer.
Above as it is explained in seen like This work packages will include :
• text renderer
• encryptor
• Password solvent
• text pointer
Logical design made encryption method mother lines with ;
1. Each One character bit on the basis It will be encrypted.
2. First stage finally produced the one which... characters entered text of your message letters will take it in order. 12x12 size matrix, the boxes are added to the selected box every time it is rotated 90 degrees. no box top on top will not overlap in the form will place it. After placing Places placed will then be marked. The checked boxes will be rotated 90 degrees clockwise. It will come after returning n will be placed in the places marked with letters. These box shapes will be rotated and repeated until they return to their original state. Then, the remaining 144-(4*n) boxes in the 12x12 dimensional box matrix will be filled with randomly generated characters. If the text to be encrypted does not fit into the matrix fields obtained with this encryption method, the use of an increasing number of matrices continues. will be done.
The resulting letters are ASCII, respectively. will be converted into codes. After the translated codes are diversified within themselves, bitmap image After it is translated, it will be sent to the other party. Then, the encrypted numbers of the fields marked in the boxes will be sent to the program as a password. Bitmap at the first stage on the receiving side The file comes in the form It will be converted into a form that the encoder can understand, then the decoder will produce the plaintext by following the steps in the encryption phase in the reverse direction.
2.3 Risk management
Risk management timing in terms of evaluated:
Project for sufficient front from research And from the preparations later there is could be risks are listed. An analysis was made regarding risk management.
Risk management there is the one which... of risks minimize to be on is focused. The risks that may occur during the project are as follows;
A: Lessons And exams therefore may occur timing obstacles
B: In the project will happen the one which... changes expected female One plan C: Lack of information about project tools
D: Project of your purpose failure to realize
TO: of the project being stolen, physically obstacles Controls will be provided through reporting.
Timing warranty as required And possible to problems opposite, official project finish from date It is planned to be completed beforehand so that any delays will not cause any problems.
Taking a project backup at every development in case of a problem that may occur in project continuity targeted.
Table one : Risk Management
2.4 Timing
Project timing in planning, may occur changes minimize to do for Long-term research was undertaken.
In the project to be done planned either in made your steps list And gantt diagram has been given. The calculation steps and results are shown below.
1. my name : Project plan
2. my name : encryption researching methods
3. my name : encryption analysis of method
4. my name : Software Modelling And design
5. my name : Text editor's realization
6. my name : Encryptions realization
7. my name : Incoming encrypted decoding the message
8. my name : test And performance measurement
9. my name : of documents preparation
Table 2: Schedule Table
2.5 Project Sources
Advisor under control Internet And library research with project continued.
Used resources listed below :
• eclipse
• Android Development tools Bundle android 4.2.1
• JDK 1.6
• WolframAlpha calculation engine
• edraw max 6.8
• SmartDraw 2012
3 THEORETICAL INFORMATIONS
Thesis in the scope of used the one which... some definitions below given:
Crude text : Will be encrypted text.
Key / Password : encryption And encrypted text in solving will be used information
Conjugate : The cell to which each selected box corresponds in the matrix every time it is rotated 90 degrees .
Page Its number : encrypted of the text occurred matrix in the number, each One adding the number of the matrix to that matrix as a page number
3.1 Suggested encryption Method
• The raw text to be encrypted will be placed in a 12x12 matrix or matrices .
• Letters of the raw text to be encrypted; It will be placed in n boxes selected according to the rule whose details will be explained later in the 12x12 matrix.
• Then, the matrix will be rotated 90 degrees clockwise to determine the boxes in which the letters are placed.
• After rotation, letters from the raw text will be placed in predetermined boxes, respectively. To avoid crushing a previously written letter of all selected boxes; When rotated 90 degrees, they should not overlap, that is, only one of the conjugate boxes can be selected so that the conjugate does not overlap with itself.
• Key matrix; It will be shifted 90 degrees clockwise 4 times until it reaches its initial position .
• If the raw text does not fit into a 12x12 matrix, the next characters are will be placed in a new matrix.
• After rotating 90 degrees 4 times, (12*12)-4n matrix boxes of the matrix, which were randomly filled with the letters of the raw text, remained empty. These empty boxes will be filled with nonsense letters, punctuation marks and spaces.
• If all the raw text ends in half of a matrix and the selected boxes are filled with randomly selected characters; To avoid problems during decryption, the location of the last character where the raw text ends in the matrix is also added to the key as information.
Details with my name step encryption;
First, when placing the raw text into 12x12 dimensional matrices, the matrix boxes in which the raw text will be placed must be selected.
If the matrix boxes to be selected overlap at every 90 degree rotation, the new letter will crush the previously written letter. Because; When selecting the boxes in which the raw text will be written, the equivalents of a selected box should not be selected again.
This to the rule suitable aspect crude text to place for sequence with;
To select the boxes in the whole matrix, we first select the boxes whose conjugates will not overlap each other from the 1st region. Each box we choose has its equivalents from the 2nd Region, 3rd Region and 4th Region. The situation is shown in Figure-8 and Figure-9
Figure-8: Developed encryption in the algorithm first key selection
One of the conjugate boxes selected from each region is randomly selected and the others are eliminated; The first letter of the raw text is placed in this box
Figure-9: Developed encryption in the algorithm second key selection
After randomly selecting a box from Region 2 as shown in the figure, we select a random box from Region 1 that has not been selected before.
We find the conjugates of the selected box in Region 1, Region 2, Region 3 and Region 4 and choose one of these conjugates to put the second character of the raw text. Thus, before the 12x12 matrix is rotated 90 degrees, we place two of the n characters to be written into the matrix.
Two character after placing later; third character to place for;
• one. from the region more before none not selected the one which... One box is selected.
• chosen box for; 2. In the region, 3. in the region And 4. in the region conjugate boxes is available.
• found boxes from random One one is selected.
• chosen This into the box crude of the text third character is placed.
Figure-10: Developed encryption in the algorithm third key selection
Fly character after placing later; fourth character to place for;
• From Region 1 more before none not selected the one which... One box is selected.
• chosen box for; 2. In the region, 3. in the region And 4. in the region conjugate boxes is available.
• found boxes from random One one is selected.
• chosen This into the box crude of the text fourth character is placed.
Figure-11: Developed encryption in the algorithm fourth key selection
Four character after placing later; fourth character to place for;
• From Region 1 more before none not selected the one which... One box is selected.
• chosen box for; 2. In the region, 3. in the region And 4. in the region conjugate boxes is available.
• found boxes from random One one is selected.
• chosen This into the box crude of the text fifth character is placed.
Figure-12: Developed encryption of the algorithm mother lines
The selection of n boxes to be selected from the 12x12 matrix is found by repeating this method n times. With this method, when the matrix is rotated 90 degrees clockwise, none of the selected boxes will crush each other. This; In the decryption method, it is important to decrypt the encrypted text without loss of characters. Because during the decryption phase, the entire matrix will be read by rotating it 90 degrees clockwise around its center.
The information to be sent as the key includes the information in which boxes the letters will be placed in the 12x12 box matrix and in which box of the last matrix the last character will be placed. is placed.
After each placement, the matrix is rotated 90 degrees clockwise. The letters following the sentence will be placed in the selected boxes starting from the [0][0] box of the matrix. The box shape that will return to the beginning after 3 turns to the right will be used and a new version will be produced in a later sentence.
Figure-13: Developed encryption of the algorithm mother lines
produced from version later 12x12 matrix symmetrical aspect information with will be filled .
The possibility of letters crushing on top of each other is prevented by the algorithm used when selecting the boxes .
If n=18 is selected in the 12x12 matrix; 18 characters will be placed in each rotation from 144 boxes.
one. 36 from the region from the box 18 grain equivalent with will be selected randomly .
After all the placements, a bitmap is created with the ASCII codes of the characters of the resulting matrices. will be obtained. This picture will be shared with the buyer.
Details with my name step encryption;
Incoming bitmap format binary string ( binary After receiving it as string ); 12x12 structure respectively to matrices characters is filled. filled characters, more previously It will be solved with the known key.
Key: It holds the information of which boxes of the matrix are selected and in which box the character of the raw text ends.
If the raw text is not long enough to fill all the boxes of the matrix; Since the boxes selected for the key will be filled with random characters; It is important to know which character the matrix ends with. If the; If this information is not used, the decrypted text will contain extra characters.
While the information about which boxes are selected from the 12x12 matrix is sent on the switch; Information about which boxes are selected will not be sent directly. Because there is a problem like the following regarding reading the key.
Key: 1234459811212...
Key This way when sent If you want to read;
(1,2), (3,4), (4,5), (9,8), (1,1), (2, 1)... and will be sent as (11,2). box (1,1) aspect will be perceived. This way wrong to analyze to obstruct Using single-digit key boxes solves the problem. For this ;
key hexadecimal at the base has been selected. in the example your key new shape;
Key: 12344598b2 c... It is in the form.
Key after being resolved later in; from bitmap get made matrices for sequence with;
• The key first tells us which boxes we need to read characters from. With the key, we first get the characters we read from the first matrix.
• Then matrix Obtained by turning 90 degrees clockwise We read the new matrix with our key and obtain new information.
• The first two characters of the information obtained are the page number in hexadecimal. We do not add this to the decoded text.
• To read characters from the first matrix for the 2nd round; matrix Obtained by turning 90 degrees clockwise again We read the new matrix with our key and obtain new information.
• To read characters from the first matrix for the 3rd round; matrix Obtained by turning 90 degrees clockwise again We read the new matrix with our key and obtain new information
• First matrix reading is carried out.
• This operations get what we do all matrices for we do.
• End matrix for Which from the box from reading we will leave control, We do this with the information at the end of the key.
Figure-14: encrypted of the text solution
As the first step to realize the coding of this developed encryption method One text regulator It was necessary. This for stated technologies with One android
virtual machine A text editor application was developed with.[7] The entered text is created as a bitmap to be encrypted with the “ Encyript ” button. It will be converted into a picture and sent to the recipient via WhatsApp on the phone. or mms It will be sent using . [8]
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 Blockchain's Revolutionary Impact on Traditional Industries and Its Adoption Challenges
Blockchain's Revolutionary Impact on Traditional Industries and Its Adoption Challenges
Medium Daily Publication
February 16, 2024
See publication
Tags: Blockchain
 Navigating the World of Academic Journal Publication: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the World of Academic Journal Publication: A Comprehensive Guide
Medium Academy
February 05, 2024
See publication
Tags: Data Center, Generative AI
 The Future of Wearable Technology: Smart Glasses by Ray-Ban and Meta
The Future of Wearable Technology: Smart Glasses by Ray-Ban and Meta
MEdium Review
February 01, 2024
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Everyday Tasks: A Statistical Overview
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Everyday Tasks: A Statistical Overview
Medium Academy
January 22, 2024
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Future of Shopping: How AI Will Shape Our Purchases
The Future of Shopping: How AI Will Shape Our Purchases
Medium News
January 19, 2024
Introduction In the digital age, the landscape of consumer behavior is undergoing a seismic shift, primarily driven by the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI is not just a buzzword; it’s rapidly becoming a crucial part of how we shop and make purchase decisions. This article explores the transformative impact of AI on consumer purchasing behavior and predicts how it will shape the future of shopping.
1. Personalized Shopping Experiences One of the most significant ways AI is changing shopping is through personalization. AI algorithms analyze a customer’s browsing history, purchase patterns, and preferences to offer tailored product recommendations. In the future, shopping platforms will become even more intuitive, predicting customer needs and preferences with unprecedented accuracy. Imagine logging onto a website and finding a curated list of products you didn’t even know you needed.
2. Enhanced Customer Service AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are revolutionizing customer service. These AI tools provide 24/7 support, answering queries, resolving issues, and offering advice, making the shopping experience smoother and more enjoyable. In the future, these AI assistants could become more sophisticated, capable of handling complex customer service tasks, reducing wait times, and improving overall customer satisfaction.
3. Smarter Inventory Management AI is also optimizing inventory management, ensuring that stores stock the right products at the right time. Predictive analytics help retailers understand buying trends, seasonal demands, and emerging patterns, enabling them to manage their inventory proactively. This efficiency not only cuts down on waste and costs but also ensures that customers find what they are looking for every time they shop.
4. Seamless Omni-channel Experience The future of shopping is not just online or in-store; it’s omni-channel. AI integrates these different channels, offering a seamless shopping experience. Whether it’s starting a shopping journey on a smartphone and finishing in a physical store, or using augmented reality (AR) to try products virtually at home, AI is at the heart of this integrated experience.
5. Price Optimization AI algorithms analyze market trends, competitor pricing, and customer demand to help retailers set the right prices. Dynamic pricing strategies enabled by AI ensure that consumers get the best value for their money, while retailers optimize their profit margins. In the future, AI-driven price optimization could become more real-time, with prices changing by the minute in response to market conditions.
Conclusion The future of shopping, shaped by AI, promises to be more personalized, efficient, and customer-friendly. As AI continues to evolve, it will offer deeper insights into consumer behavior, leading to more innovative and responsive shopping experiences. However, with these advancements come challenges around data privacy and the need for ethical AI practices. Balancing innovation with responsibility will be key to harnessing the full potential of AI in shaping future purchasing behaviors. As we stand on the brink of this AI-driven retail revolution, one thing is certain: shopping as we know it is set to transform dramatically.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 “The Transformative Power of Blockchain in the Global Economy”
“The Transformative Power of Blockchain in the Global Economy”
Medium
January 10, 2024
In an era where digital technology is reshaping the global economic landscape, blockchain technology emerges as a groundbreaking innovation. Initially associated with cryptocurrencies, blockchain has now found applications far beyond its initial use in finance. This article delves into how blockchain is influencing various sectors, fostering transparency, security, and efficiency.
Blockchain in Finance: Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): A deep dive into how blockchain-powered DeFi is challenging traditional banking models, offering decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading.
Cross-Border Payments: Discussion on how blockchain simplifies international transactions, reducing time and costs, and enhancing security.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
Traceability and Transparency: Examining case studies where blockchain is used for tracking products from origin to consumer, enhancing supply chain visibility.
Fraud Prevention: How blockchain’s immutable ledger reduces the risk of counterfeit goods and fraud in supply chains.
Advancements in Healthcare
Secure Patient Data: Exploration of blockchain’s role in protecting patient data and enabling secure data sharing across healthcare providers.
Drug Traceability: Analysis of blockchain’s application in tracking pharmaceuticals to ensure authenticity and combat counterfeit drugs.
Blockchain for Social Impact
Voting Systems: Insights into how blockchain can revolutionize voting mechanisms, ensuring transparency and reducing electoral fraud.
Charitable Donations: Case studies on blockchain’s use in tracking charitable contributions to ensure they reach the intended beneficiaries.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Scalability Issues: Discussing the challenges blockchain faces in terms of scalability and energy consumption.
Regulatory Landscape: A look at how different countries are approaching blockchain regulation and the impact on innovation.
Future Trends: Predictions about the evolution of blockchain technology, including potential breakthroughs and emerging sectors.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is not just a fleeting trend; it represents a paradigm shift in how we approach data security, transparency, and transactions across various industries. As blockchain continues to evolve, its potential to transform the global economy becomes increasingly apparent.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
Exploring the Future: Jobs Created by Artificial Intelligence
Google Blog
December 21, 2023
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands out as a revolutionary force, reshaping how we live and work. While there's a common fear that AI might lead to job loss, it's equally important to recognize the myriad of new job opportunities it is creating. Let's delve into the types of jobs we can expect AI to generate in the future.
1. AI Trainers and Explainers
As AI systems become more complex, the need for AI trainers, who teach AI algorithms how to process and interpret data, will rise. These professionals will be responsible for 'training' AI systems in language nuances, social dynamics, and ethical considerations. Alongside them, AI explainers will emerge to bridge the gap between technologists and business leaders, explaining AI processes and decisions in a digestible manner.
2. AI Maintenance and Management Specialists
The rise of AI will also create demand for specialists focused on the maintenance and management of AI systems. These roles will include monitoring AI systems for errors or anomalies, updating systems with new data, and ensuring optimal performance. This field will require a blend of technical skills and an understanding of the AI lifecycle.
3. Data Scientists and Analysts
Data is the lifeblood of AI. As AI applications proliferate, the demand for data scientists and analysts will surge. These professionals will be responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large datasets to aid in AI model development and decision-making processes.
4. Ethical Compliance Officers
The ethical implications of AI are profound. Ethical compliance officers will play a critical role in ensuring that AI applications adhere to ethical standards and regulatory requirements. They will assess AI systems for biases, privacy concerns, and ethical risks, ensuring responsible AI deployment.
5. AI-Enhanced Healthcare Professionals
In healthcare, AI is set to revolutionize diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. Future roles might include AI-enhanced healthcare professionals who use AI tools for patient diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring, bringing more precision and efficiency to healthcare services.
6. AI Integration Specialists
As AI technologies become more integrated into various industries, specialists will be needed to oversee the seamless integration of AI into existing business processes and workflows. This role will require a strong understanding of both AI technology and industry-specific knowledge.
7. Customer Experience Managers with AI Expertise
In the realm of customer service, AI is already making inroads. Future customer experience managers will need to understand how to leverage AI tools like chatbots and virtual assistants to enhance customer interactions and improve service efficiency.
8. Personalized Education Facilitators
AI is poised to personalize education, making learning more adaptive and individualized. Educators and facilitators skilled in AI tools will be crucial in developing and implementing personalized learning plans for students, utilizing AI to cater to individual learning styles and needs.
9. AI-Centric Content Creators
In media and content creation, AI is already being used to generate news articles, music, and art. Future roles might include AI-centric content creators who understand how to collaborate with AI tools to produce unique and innovative content.
Conclusion
The advent of AI is not just a tale of automation and job displacement, but one of transformation and job creation. The future will require a workforce skilled in AI and its applications, blending technical knowledge with creativity, ethical understanding, and domain-specific expertise. As we embrace AI, we open the doors to new career paths and opportunities, heralding a future where human ingenuity and AI innovation work hand in hand.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
In the contemporary business landscape, big data analytics has emerged as a powerful tool for companies to gain a competitive edge. Here's a brief exploration of how businesses can harness this technology:
iibf antep
December 14, 2023
In the contemporary business landscape, big data analytics has emerged as a powerful tool for companies to gain a competitive edge. Here's a brief exploration of how businesses can harness this technology:
1. Personalized Customer Experiences: By analyzing customer data, companies can tailor their products and services to meet individual preferences, thus enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Efficient Decision-Making: Big data analytics enables businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time insights, leading to more effective strategies and operational efficiencies.
3. Predictive Analysis: Companies can anticipate market trends and consumer behavior, allowing them to be proactive rather than reactive in their business approaches.
4. Enhanced Marketing Strategies: Through the analysis of customer data, businesses can develop targeted marketing campaigns that resonate more effectively with their audience.
5. Risk Management: Big data analytics helps in identifying potential risks and formulating strategies to mitigate them, ensuring long-term sustainability.
6. Streamlining Operations: By analyzing operational data, businesses can identify inefficiencies and optimize their processes for better performance and reduced costs.
In conclusion, big data analytics is not just a technological tool, but a strategic asset that can drive innovation, efficiency, and growth for businesses in the digital era.
See publication
Tags: AI, Data Center, Marketing
 Managing Big Data with SQL and Databases
Managing Big Data with SQL and Databases
University of Gaziantep
December 13, 2023
Managing Big Data with SQL and Databases
In the era of big data, efficiently managing and extracting meaningful insights from massive datasets has become a critical task for businesses and organizations. SQL (Structured Query Language) and database management systems are at the forefront of this challenge, offering robust solutions for handling big data. This blog post explores the principles of managing big data with SQL and databases, highlighting best practices, challenges, and potential strategies.
Understanding Big Data
Before diving into the management strategies, it's crucial to understand what big data entails. Big data refers to datasets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing software to handle. This data can come from various sources like social media, transaction records, IoT devices, and more. The challenge lies in processing, storing, and analyzing this data efficiently.
The Role of SQL in Big Data
SQL, a language designed for managing and querying data in relational database management systems (RDBMS), remains vital in the big data landscape for several reasons:
Structured Querying: SQL provides a structured approach to query large datasets, enabling users to retrieve specific data swiftly.
Compatibility: Many big data processing tools and platforms integrate SQL or SQL-like querying capabilities, making it a versatile choice.
Data Manipulation and Analysis: SQL is not just for querying; it's also effective for data manipulation and complex analyses, which are essential in big data environments.
Database Management Systems for Big Data
Choosing the right database management system is crucial for big data applications. There are mainly two types of databases used:
Relational Databases (RDBMS): Traditional databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. They are schema-based and use SQL for querying.
NoSQL Databases: These databases, such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and HBase, are designed for unstructured data and can handle large volumes of data more efficiently in certain scenarios.
Best Practices for Managing Big Data with SQL and Databases
Data Modeling: Proper data modeling is essential for both RDBMS and NoSQL databases. It involves defining how data is stored, accessed, and managed.
Scalability: Ensure the database can scale horizontally to manage increased data loads.
Indexing: Effective indexing strategies are crucial for optimizing query performance in large datasets.
Partitioning: Partitioning data across different tables or databases can significantly improve performance.
Regular Maintenance: Routine maintenance activities like indexing, data archiving, and cleanup are vital for optimal performance.
Security: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive big data.
Overcoming Challenges
Managing big data with SQL and databases comes with its challenges:
Handling Unstructured Data: SQL databases are traditionally designed for structured data. Integrating NoSQL solutions can help in managing unstructured data efficiently.
Performance Optimization: As data volume grows, performance tuning becomes crucial. This includes optimizing queries, improving database design, and leveraging caching.
Real-Time Processing: Big data often requires real-time processing. Technologies like Apache Kafka and streaming SQL can help in achieving real-time data processing and analytics.
The Future of Big Data with SQL and Databases
The future of big data management is geared towards more integrated solutions. Technologies like NewSQL are emerging, combining the scalability of NoSQL with the consistency and structured querying of SQL databases. Moreover, advancements in cloud-based database solutions and machine learning integration will continue to shape how we manage and leverage big data.
Conclusion
Managing big data with SQL and databases requires a strategic approach, understanding of the right tools, and adherence to best practices. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the role of SQL and databases remains pivotal in unlocking the true potential of big data. Whether it's through traditional RDBMS or more recent NoSQL technologies, the goal is to extract actionable insights from large datasets while ensuring efficiency, scalability, and security.
See publication
Tags: AI, Blockchain, Data Center
 Navigating the Horizon: The Future of AI and Its Impact on Humanity
Navigating the Horizon: The Future of AI and Its Impact on Humanity
Google
December 12, 2023
Navigating the Horizon: The Future of AI and Its Impact on Humanity
As we sail into the future, the winds of artificial intelligence (AI) are blowing us towards an unknown horizon with promises of transformation unlike anything we've witnessed before. The future of AI is not just an extension of its current capabilities, but a leap into a world where it touches every aspect of our lives. Let's explore what this future might look like and how it could reshape our world.
Autonomous Evolution
The AI of tomorrow will evolve beyond programmed algorithms to autonomous entities capable of self-improvement. These systems will not just learn from the data fed into them but will also be able to set their own goals, assess their performance, and iterate their processes—all without human intervention. Imagine an AI that can invent new scientific theories or create art that resonates with human emotions, blurring the lines between creator and creation.
Synergy in the Workplace
AI's integration into the workplace is set to revolutionize how we work. While some fear the obsolescence of human roles, the future likely holds a more synergistic relationship between humans and AI. This partnership will see humans providing the strategic direction and emotional intelligence, while AI offers unparalleled efficiency and data processing capabilities. The result? A more productive, creative, and dynamic workforce.
Personalized Experiences
Consumer experiences are becoming increasingly personalized, thanks to AI. In the future, AI could curate every aspect of our lives, from the entertainment we consume to the food we eat, tailored to our individual preferences and even our health needs. This level of personalization could extend to education, where AI tutors could provide bespoke learning experiences that adapt to each student's learning style and pace.
Ethical and Moral Questions
As AI grows more powerful, the ethical and moral implications of its decisions will come to the forefront. The future will demand a robust framework for AI ethics, addressing issues such as privacy, autonomy, and the potential for AI to perpetuate biases. The governance of AI will become a critical global conversation, shaping policies that ensure the technology is used responsibly and for the greater good.
Augmented Reality
AI will be pivotal in advancing augmented reality (AR). Future AR systems, powered by AI, could provide real-time information overlays and assist in complex tasks, from surgery to space exploration. This fusion of AI and AR has the potential to enhance our senses and perceptions, effectively expanding the limits of human capability.
Health and Longevity
AI's impact on healthcare could be revolutionary, offering diagnostics with precision beyond human capabilities, personalized medicine, and even AI-assisted surgery. In the future, AI might manage our health maintenance, predict potential illnesses before they manifest, and extend our lifespan through advanced understanding of aging and disease.
A World of AI Governance
To manage the widespread influence of AI, we may see the emergence of AI governance bodies. These organizations will not only regulate the development and deployment of AI but also ensure that AI operates in alignment with human values and societal norms.
Final Thoughts
Predicting the future of AI is a complex and uncertain endeavor. However, one thing is clear: AI's journey is intertwined with our own. As we step into this new era, we must tread thoughtfully, embracing the potential of AI to enhance our lives while remaining vigilant about steering its course responsibly. In the symphony of progress, AI is both the instrument and the composer, and it's up to us to ensure that the music it creates is harmonious and enriching for all of humanity.
See publication
Tags: AI, Blockchain, Data Center
Mastering Leadership: Essential Skills for Software and Data Scientist Employees
simplified
November 28, 2023
1. Introduction
In today's highly competitive job market, having technical skills alone is no longer enough to excel in the field of software and data science. Employers are increasingly looking for individuals who not only possess strong technical knowledge but also demonstrate effective leadership skills. Mastering leadership is essential for software and data scientist employees to thrive in their careers and make a significant impact in their organizations. This blog will explore the essential leadership skills that software and data scientist employees need to develop and how these skills can enhance their professional growth and success.
2. The importance of leadership in software and data scientist roles
In the ever-evolving world of technology, software and data scientist roles have become widely sought after. These professionals are instrumental in developing innovative software solutions and extracting valuable insights from complex data sets. While technical expertise is undoubtedly crucial in these roles, the importance of leadership cannot be underestimated.
Effective leadership skills allow software and data scientists to not only excel individually but also inspire and guide their teams towards success. As leaders, they are responsible for setting clear goals, motivating team members, and fostering a collaborative and creative work environment. Additionally, their ability to communicate effectively and make strategic decisions is integral in driving projects forward and ensuring their successful completion.
Moreover, leadership skills empower software and data scientists to take initiative, think critically, and adapt to changing circumstances. They enable professionals to navigate challenges and drive innovation, ultimately leading to increased efficiency and productivity within an organization.
In the next section, we will explore the specific leadership skills that software and data scientist employees should develop to thrive in their roles and make a lasting impact. Stay tuned!
3. Essential skills for software and data scientist leaders
Next section: Essential skills for software and data scientist leaders
To truly master leadership in the software and data scientist field, there are specific skills that professionals should focus on developing. These essential skills will not only enhance their individual performance but also empower them to effectively lead their teams.
1. Strategic thinking: Software and data scientist leaders need to have the ability to think strategically. This involves understanding the big picture, anticipating future trends and challenges, and formulating effective strategies to overcome them. By having a long-term perspective, leaders can make informed decisions that align with the organization's goals and objectives.
2. Emotional intelligence: A high level of emotional intelligence is crucial for leaders in any industry, including software and data science. Being able to understand and manage one's own emotions, as well as the emotions of others, fosters positive and productive relationships. Leaders with strong emotional intelligence can effectively communicate, collaborate, and build trust with their team members.
3. Problem-solving: As software and data scientist leaders, being skilled problem solvers is essential. They need to have the ability to analyze complex issues, identify solutions, and make informed decisions. Effective problem-solving skills enable leaders to navigate challenges and find innovative solutions that drive projects forward.
4. Communication: Clear and effective communication is a fundamental skill for leaders in any field. Software and data scientist leaders must be able to articulate their ideas, expectations, and goals to their team members. Additionally, they need to actively listen and provide constructive feedback to foster a collaborative work environment.
By cultivating these essential skills, software and data scientist leaders can not only excel in their roles but also drive their teams towards success. In the next section, we will delve deeper into each of these skills and provide practical tips on how to develop them. Stay tuned!
4. Developing effective communication and collaboration
Next section: Developing effective communication and collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial skills for software and data scientist leaders to master. In today's fast-paced and highly collaborative work environment, leaders must be able to effectively communicate their ideas, expectations, and goals to their team members.
One key aspect of effective communication is being able to articulate information clearly and concisely. Leaders should strive to use simple and straightforward language that is easily understandable by team members. This helps to avoid misunderstandings and ensures everyone is on the same page.
Active listening is another essential component of effective communication. Leaders should listen attentively to their team members, giving them their full attention and showing empathy and understanding. By actively listening, leaders can gain valuable insights, resolve conflicts, and build trust within the team.
Collaboration is equally important in the software and data scientist field. Leaders should encourage teamwork and foster a collaborative work environment where employees can freely share ideas, provide feedback, and contribute to the overall project success. By fostering a culture of collaboration, leaders can harness the collective intelligence of their team and drive innovation.
In the next section, we will explore practical strategies for developing effective communication and collaboration skills in software and data scientist leaders. Stay tuned to learn how you can enhance your leadership abilities in these crucial areas.
5. Nurturing problem-solving and critical thinking skills
Developing problem-solving and critical thinking skills is imperative for software and data scientist leaders. In today's complex and dynamic work environment, leaders must be able to analyze challenges, think creatively, and come up with innovative solutions.
One important aspect of nurturing problem-solving skills is encouraging a growth mindset. Leaders should foster a culture where mistakes are seen as learning opportunities and where employees are empowered to think outside the box. By embracing a growth mindset, leaders can inspire their team members to take risks, experiment with new ideas, and overcome obstacles.
Additionally, leaders should provide the necessary resources and support for their team to develop critical thinking skills. This includes providing access to training programs, workshops, and educational resources that promote analytical thinking and problem-solving techniques. Leaders should also encourage the exploration of different perspectives and encourage their team members to challenge assumptions and think critically about complex issues.
By nurturing problem-solving and critical thinking skills, software and data scientist leaders can equip their team with the tools they need to tackle complex challenges and drive innovation. In the next section, we will delve deeper into specific strategies for developing these skills. Stay tuned to discover practical tips for enhancing your problem-solving and critical thinking abilities as a leader in the software and data scientist field.
6. Empowering and motivating team members
Empowering and motivating team members is a crucial aspect of effective leadership in the software and data scientist field. When employees feel empowered and motivated, they are more likely to be engaged, productive, and committed to their work.
To empower team members, leaders can delegate responsibilities and give individuals the autonomy to make decisions and take ownership of their work. Trusting employees to make important decisions not only boosts their confidence but also encourages them to think critically and come up with innovative solutions.
In addition to empowerment, motivation plays a key role in driving performance. Leaders can motivate their team by recognizing and rewarding their contributions, providing clear goals and expectations, and fostering a positive work environment. Regular communication, feedback, and mentorship opportunities are also important factors in keeping team members motivated and inspired.
By empowering and motivating their team members, software and data scientist leaders can create a culture of high performance and continuous growth. In the next section, we will explore strategies for effective delegation and motivating team members to achieve their full potential. Stay tuned for practical tips on how to empower and motivate your team in the software and data scientist field.
See publication
Tags: Big Data, Data Center, Leadership
Blockchain technology has gained attention for its potential to disrupt various industries by providing a secure and transparent way to record and verify transactions. Some of the best-known applications of blockchain technology and the ones that have shown promise include
Youtube Academy
November 01, 2023
Cryptocurrencies:
Bitcoin: The original and most well-known cryptocurrency, Bitcoin uses blockchain to enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
Smart Contracts:
Ethereum: Ethereum introduced the concept of smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract written into code. This has applications in areas like decentralized finance (DeFi) and supply chain management.
Supply Chain Management:
Provenance: Blockchain is used to track the origin and journey of products, ensuring authenticity and transparency in the supply chain.
Identity Verification:
Civic: Blockchain technology is used to securely verify and store personal identity information, reducing the risk of identity theft.
Voting Systems:
Voatz: Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, enhancing the integrity of elections.
Real Estate:
Propy: Blockchain can simplify and secure real estate transactions, making the process more efficient.
Healthcare:
MedicalChain: Blockchain is used to securely store and share patient medical records, enhancing data security and interoperability.
Cross-Border Payments:
Ripple: Blockchain is utilized to facilitate fast and low-cost cross-border payments and remittances.
Digital Ownership and Collectibles:
CryptoKitties: Blockchain-based games and platforms allow users to own and trade digital assets securely.
Legal and Notary Services:
Uport: Blockchain can provide secure and tamper-proof notarization and legal document services.
Intellectual Property Protection:
Mycelia: Musicians and artists can use blockchain to manage their intellectual property rights and royalties.
Energy Trading:
Power Ledger: Blockchain can enable peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to buy and sell excess energy directly.
Agriculture:
AgriDigital: Blockchain is used for tracking and verifying the origin of agricultural products and ensuring transparency in the supply chain.
Insurance:
Lemonade: Blockchain can streamline and automate insurance processes, making them more efficient and transparent.
Education:
Learning Machine: Blockchain can be used to store and verify academic credentials and certifications.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of blockchain technology. The effectiveness of a blockchain solution depends on factors like network security, consensus mechanisms, and adoption within the industry. Blockchain technology is still evolving, and its potential continues to be explored in various sectors, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges.
See publication
Tags: AI, Blockchain, Digital Transformation
 Latest inventions in the marketing
Latest inventions in the marketing
Linkedin
October 22, 2023
See publication
Tags: Agile, Innovation, Marketing
In a world where digital innovation is constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force that promises to reshape industries and redefine the way we think about trust and security
İstanbul Technical University
May 16, 2023
Introduction
In a world where digital innovation is constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force that promises to reshape industries and redefine the way we think about trust and security. Blockchain has garnered significant attention in recent years, and it's not just because of its association with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Its potential extends far beyond digital currencies, touching industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more. In this blog, we'll delve into the world of blockchain, demystify its underlying principles, explore its applications, and discuss its future implications.
What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure and tamper-proof manner. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single entity has control over the ledger, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring transparency and trust among participants.
Key Components of Blockchain:
Blocks: Transactions are grouped into blocks, which are essentially data containers. Each block contains a set of transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block, creating a chronological chain of blocks.
Decentralization: Instead of relying on a central authority, blockchain relies on a network of nodes (computers) that validate and record transactions. This decentralization makes it resistant to censorship and tampering.
Cryptography: Transactions on the blockchain are secured through cryptographic techniques. Each participant has a public key (like an address) and a private key (a secret code). These keys ensure the security and privacy of transactions.
Consensus Mechanism: To agree on the state of the blockchain, nodes in the network must reach consensus. The most well-known consensus mechanism is Proof of Work (PoW) used in Bitcoin, but there are others like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency
While Bitcoin introduced the world to blockchain, its applications are not limited to digital currencies. Here are some prominent use cases:
Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code have found applications in legal, real estate, and supply chain industries. They automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track the origin and journey of products in real-time, ensuring transparency and authenticity. This is particularly valuable in industries like food and pharmaceuticals.
Healthcare: Patient records can be securely and efficiently managed on a blockchain, ensuring interoperability and privacy while reducing administrative costs.
Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems have the potential to eliminate voter fraud and increase transparency in elections.
Finance: Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is transforming traditional finance with faster, more secure cross-border payments and the creation of digital assets.
Challenges and Future Directions
Blockchain is not without its challenges. Scalability, energy consumption (in PoW systems), and regulatory concerns are areas that need addressing. However, ongoing research and development are actively working to overcome these hurdles.
The future of blockchain looks promising. It may become a fundamental infrastructure for the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling secure data exchange between devices. Moreover, as blockchain technology matures and becomes more user-friendly, it could see widespread adoption in various industries, bringing about greater efficiency, transparency, and security.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is undeniably one of the most exciting innovations of our time. Its potential to disrupt traditional systems and establish trust in an increasingly digital world is immense. While it's still evolving, blockchain is poised to transform industries, creating a future where decentralized, transparent, and secure systems are the norm. As we navigate this blockchain-driven future, it's essential to stay informed and explore the numerous opportunities it presents.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Change Management, IoT
 What is the Scrum
What is the Scrum
Medium Daily Blog
December 31, 1969
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Daily Integration of AI: Transforming Lives and Industries
The Daily Integration of AI: Transforming Lives and Industries
Medium Author newsletter
February 21, 2024
In the modern world, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from a futuristic concept to a practical tool deeply embedded in our daily lives. This transformation is not just limited to tech industries but spans across various sectors including healthcare, finance, education, entertainment, and even our personal routines. This report delves into the pervasive use of AI, illustrating its impact and the subtle ways it shapes our day-to-day experiences.
Personal and Home Use
At the individual level, AI has made significant inroads into our homes and personal devices. Smart assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri have become household names, offering voice-activated help ranging from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices. These assistants learn from our preferences to provide tailored information, such as news, weather updates, and traffic conditions, making daily routines more efficient.
AI-driven recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon have transformed entertainment and shopping by analyzing our past behavior to suggest movies, music, or products we might like. This personalization enhances user experience and engagement, making these platforms indispensable in our leisure and consumption habits.
Healthcare
In healthcare, AI is revolutionizing diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with accuracy that matches or surpasses human experts. This capability speeds up diagnosis, aids in early detection of diseases like cancer, and personalizes treatment plans. AI-powered chatbots and virtual health assistants provide 24/7 support and information to patients, improving healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
Finance and Banking
The finance sector has embraced AI for fraud detection, risk management, and customer service. AI systems analyze transaction patterns to identify and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time. They also assist in assessing loan applications, predicting risks, and making investment decisions based on vast amounts of data. Chatbots and virtual assistants are now common in banking, offering instant responses to customer inquiries and facilitating transactions without human intervention.
Education
AI is transforming education through personalized learning platforms that adapt to each student’s pace and style of learning. These platforms can identify strengths and weaknesses, suggesting resources to improve learning outcomes. Moreover, AI tools assist teachers in grading and administrative tasks, allowing them to devote more time to teaching and student interaction.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, the integration of AI into daily life raises privacy, security, and ethical concerns. The collection and analysis of personal data by AI systems pose risks if not properly managed. There is also the challenge of ensuring AI decisions are fair, transparent, and accountable, especially in critical areas like healthcare and law enforcement.
Conclusion
The daily use of AI is reshaping our world, offering conveniences and efficiencies previously unimaginable. As we continue to navigate its integration, the focus must remain on harnessing its potential responsibly, ensuring it serves to enhance human capabilities and well-being. The future of AI is not just about technological advancement but about creating a symbiotic relationship between humans and machines, enriching lives and opening new frontiers across all sectors of society.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 Unveiling the Convergence: Data and Blockchain Technologies
Unveiling the Convergence: Data and Blockchain Technologies
Medium Education
February 19, 2024
Unveiling the Convergence: Data and Blockchain Technologies
In the digital era, where data is as valuable as currency, the significance of secure, transparent, and immutable data management systems cannot be overstated. Enter blockchain technology, a revolutionary approach to secure digital transactions, which has shown a promising potential to redefine not just the financial sector but various data-intensive industries. At their core, data and blockchain technologies share fundamental principles and challenges, and their convergence could pave the way for a new era of digital innovation and security.
Shared Foundations
Decentralization
At the heart of blockchain technology lies the principle of decentralization. Unlike traditional data management systems that rely on a central authority, blockchain distributes its operations across a network of computers. This paradigm shift not only enhances security by eliminating single points of failure but also democratizes data access, making information verification a collective process.
Transparency and Trust
Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This level of transparency builds trust among users, as every transaction is verifiable and permanent. Similarly, data technologies strive for transparency to ensure accuracy and reliability, principles that are becoming increasingly important in an age of misinformation.
Security
Security is a paramount concern for both data and blockchain technologies. Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data transactions, providing a robust defense against tampering and fraud. Data technologies, in turn, employ various security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches, aiming for a level of security that blockchain naturally embeds in its architecture.
Converging Paths
Enhanced Data Integrity
The integration of blockchain into data management systems can significantly enhance data integrity. By leveraging blockchain's immutable ledger, data recorded in any system becomes tamper-evident. This capability is invaluable for industries where data authenticity and audit trails are critical, such as healthcare, legal, and finance.
Improved Data Sharing
Blockchain can revolutionize data sharing between organizations. With its decentralized nature, blockchain creates a secure and efficient environment for data exchange, free from intermediaries. This not only reduces the risk of data breaches but also streamlines operations, making inter-organizational data sharing more straightforward and trustworthy.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain introduces the concept of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This innovation can automate various data-driven processes, ensuring compliance and execution without the need for intermediaries. From automating payments upon fulfilling data verification to enforcing data usage policies, smart contracts represent a significant step towards autonomous and secure data management systems.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their shared benefits, the integration of data and blockchain technologies faces challenges. Scalability remains a concern for blockchain, as increasing the number of transactions can lead to network congestion and higher costs. Additionally, privacy issues arise due to the transparent nature of blockchain, necessitating solutions that balance transparency with confidentiality.
Moreover, regulatory challenges cannot be ignored. As both technologies continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks must adapt to address the unique aspects of blockchain-based data management, ensuring compliance while fostering innovation.
Conclusion
The convergence of data and blockchain technologies offers a promising avenue for enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency in digital transactions and data management. As industries continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, the principles shared by data and blockchain technologies could serve as a beacon for developing secure, efficient, and transparent systems. Embracing this convergence will require overcoming technical, privacy, and regulatory challenges, but the potential rewards—a more secure, transparent, and efficient digital future—are undoubtedly worth the effort.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Dawn and Future Horizon of Artificial Intelligence: A Journey from Simple Algorithms to Advanced AI
The Dawn and Future Horizon of Artificial Intelligence: A Journey from Simple Algorithms to Advanced AI
Medium Platform
January 11, 2024
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed from a fantastical concept into a fundamental part of our daily lives. This article explores the evolution of AI from its inception to its current state and projects its potential future developments.
The Starting Point: Early Days of AI
The journey of AI began in the mid-20th century, rooted in the question posed by Alan Turing: “Can machines think?” The 1950s and 60s witnessed the birth of AI as a field of study, marked by early programs like the Turing Test and ELIZA, an early natural language processing computer program.
The 1970s to 1990s: Expansion and Hibernation
AI’s initial progress faced challenges due to limited computational power and understanding. The 1970s saw AI’s first winter — a period of reduced funding and interest. However, the 1980s experienced a resurgence with the development of expert systems, only to be followed by another AI winter in the late 1980s.
The 21st Century: The AI Renaissance
The resurgence of AI in the early 21st century was fueled by increased computational power, the advent of the internet, and breakthroughs in machine learning and neural networks. AI’s application expanded, influencing sectors like healthcare, finance, and transportation.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning: The Game Changers
Machine learning, a subset of AI, enabled systems to learn and improve from experience. The introduction of deep learning architectures, like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), further revolutionized AI’s capabilities.
The Current State: AI in Daily Life
Today, AI is omnipresent. From personal assistants like Siri and Alexa to more complex systems like autonomous vehicles and predictive analytics in healthcare, AI’s integration into daily life is profound.
Ethical Considerations and AI
As AI becomes more advanced, ethical concerns, including privacy, bias, and job displacement, have emerged. Addressing these issues is crucial for the responsible development and implementation of AI technologies.
The Future of AI: Predictions and Possibilities
General AI: The pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), machines with the ability to understand, learn, and apply intelligence broadly across a range of tasks, remains a key goal.
Quantum AI: Quantum computing promises to offer exponential growth in computational power, potentially revolutionizing AI’s problem-solving capabilities.
AI in Healthcare: Advanced diagnostic tools, personalized medicine, and robotic surgery are areas where AI could significantly impact healthcare.
AI and IoT: The integration of AI with the Internet of Things (IoT) could lead to smarter cities, more efficient energy use, and enhanced security systems.
Conclusion
The development of AI has been a journey of peaks and valleys. From simple algorithms to sophisticated machine learning models, AI has grown exponentially. Its future, teeming with possibilities, poses exciting opportunities and significant challenges. As we stand on the brink of further AI advancements, it is crucial to guide this development with careful consideration of ethical implications to harness the full potential of AI for the betterment of society.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
Future of AI
Supply Chain Clup of Yıldız Teknik University
March 09, 2024
ntroduction Slide:
[Opening Image: A professional, engaging photo of the speaker]
Slide 1: Welcome & Introduction
Text: "Welcome to Supply chain clup of Yildiz Teknik University
Subtext: "Empowering Insights, Inspiring Ideas"
Slide 2: Introducing Our Keynote Speaker
Text: "We are honored to present our keynote speaker, Osman Kıvanç çengel
Subtext: "A Visionary in Artifical Intelligence
Slide 3: Expertise & Achievements
Bullet Points Highlighting Speaker's Credentials:
"Renowned Business Development professional with over 8 years of experience."
"Recipient of Globee, recognizing their contributions to IT
"Leading voice in artifical intelligence, with numerous publications in top journals."
Slide 4: Speaker's Vision
Text: "AI future's vision "
Subtext: "Transforming AI in daily work through innovation and insight."
Slide 5: Why Listen?
Bullet Points on Why the Audience Should Engage:
"Gain cutting-edge insights into Future of AI"
"Learn actionable strategies for AI using and app
"Inspire change and innovation within your own Career.
Slide 6: Join Us
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Future of Generative AI: Transforming the Way We Create and Interact
The Future of Generative AI: Transforming the Way We Create and Interact
blog of google
December 15, 2023
The Future of Generative AI: Transforming the Way We Create and Interact
Generative AI, the technology behind creating content autonomously, has already made significant strides in transforming various industries. From writing assistance to image generation and beyond, the capabilities of generative AI continue to expand. But what does the future hold for this groundbreaking technology? Let's explore the potential developments and implications of generative AI in the coming years.
Enhanced Creative Collaboration
Generative AI will not replace human creativity but augment it. Artists, writers, and designers will use AI as a collaborative tool to push the boundaries of their creativity. Imagine a scenario where an AI not only suggests improvements to a novel’s plot but also creates immersive virtual worlds for the reader, enhancing storytelling with a multi-sensory experience.
Personalized and Adaptive Learning
In education, generative AI could offer personalized learning experiences. It might adapt educational content to match a student's learning style and pace, making education more accessible and effective. AI tutors could provide real-time help, ensuring no student falls behind due to a lack of resources.
Revolutionizing Healthcare
Generative AI could significantly impact healthcare by personalizing patient treatment plans and simulating medical outcomes. It may help in drug discovery by predicting molecular responses, reducing the time and cost of developing new medicines. AI could also generate virtual models of patients' organs for surgeons to practice on before actual surgery.
Ethical and Responsible Use
As generative AI becomes more advanced, ethical considerations will take center stage. The technology raises questions about authenticity, privacy, and bias. Ensuring AI-generated content is used ethically and responsibly will be crucial. This includes preventing the spread of misinformation and protecting intellectual property rights.
Advancements in AI Governance
With the growing use of generative AI, there will be a need for robust AI governance frameworks. Regulations may be introduced to address issues like data privacy, security, and the ethical use of AI. These measures will ensure that AI benefits society while mitigating potential risks.
Integration into Daily Life
Generative AI will become more integrated into our daily lives. We could see AI personal assistants that not only respond to our queries but anticipate our needs and preferences. AI could manage our schedules, suggest meals based on our health goals, and even help in personalizing our fitness routines.
Real-time Language Translation
The future of generative AI also includes breaking down language barriers. Real-time, accurate translation services will enable seamless communication between people from different linguistic backgrounds, fostering global collaboration and understanding.
Challenges and Opportunities
As with any technological advancement, generative AI will present challenges. There will be a continuous need to balance innovation with ethical considerations. Job displacement is a concern, but new roles will emerge in AI supervision, training, and ethics. The key will be in adapting to these changes and leveraging AI to create new opportunities.
Conclusion
The future of generative AI is not just about technological advancements; it's about how we harness these advancements to improve our lives, work, and society. By emphasizing ethical use, continuous learning, and adaptation, generative AI can be a powerful tool in shaping a future that's innovative, inclusive, and responsive to human needs.
As we stand on the brink of these exciting developments, one thing is clear: generative AI is not just a fleeting trend but a transformative force that will redefine the landscape of human-machine interaction for years to come.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 The Expansive Future of Blockchain Across Industries
The Expansive Future of Blockchain Across Industries
bdsgrp uk
December 04, 2023
The Expansive Future of Blockchain Across Industries
Blockchain technology, best known as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is set to revolutionize a wide range of sectors. Its unique capabilities in ensuring transparency, security, and decentralization make it an attractive solution for various applications beyond digital currencies. Here's a closer look at the industries that are poised to be transformed by blockchain technology in the future.
Financial Services: A New Era of Transactions
Blockchain's initial and most notable impact has been in the financial sector. It offers a secure and efficient way to handle transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries like banks. We can expect further advancements in peer-to-peer payments, cross-border transactions, and more innovative financial products like decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions, which aim to provide a full spectrum of financial services, from banking to lending and investing, without the need for traditional financial institutions.
Supply Chain Management: Enhancing Transparency and Efficiency
The supply chain industry stands to gain significantly from blockchain technology. By enabling transparent tracking of products from manufacture to delivery, blockchain can help ensure authenticity and compliance, combat counterfeit goods, and enhance efficiency. For industries like pharmaceuticals, where product authenticity is critical, blockchain can provide a foolproof way to track the lifecycle of products.
Healthcare: Securing Patient Data
In healthcare, managing and securing patient data is paramount. Blockchain can offer a solution to securely store health records, allowing for controlled access while maintaining patient privacy. This could revolutionize patient data management, making it more efficient, secure, and patient-centric.
Real Estate: Streamlining Transactions
The real estate sector can benefit from blockchain in streamlining property transactions. By maintaining secure and transparent records of property ownership and history, blockchain can reduce fraud, expedite property transfers, and simplify record-keeping. This technology could also make real estate investments more accessible through tokenization, dividing property into tradable shares or tokens.
Voting Systems: Ensuring Integrity and Accessibility
Blockchain could transform voting systems by offering a secure, transparent, and easily verifiable way to conduct elections. This can help to reduce electoral fraud, increase voter turnout by making voting more accessible, and boost public trust in the electoral process.
Intellectual Property and Copyright Management
For artists, musicians, and writers, blockchain presents a new way to manage and protect intellectual property. It can be used to prove ownership, manage and enforce copyright agreements, and ensure fair compensation for creators through smart contracts.
Energy Sector: Decentralizing Energy Distribution
Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt the energy sector by enabling peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to buy and sell excess energy directly with each other. This could lead to more efficient use of renewable energy sources and potentially lower costs.
Conclusion: A Blockchain-Driven Future
As blockchain technology continues to mature, its applications across various industries are likely to expand. The promise of enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency is too significant to ignore. While challenges remain, such as scalability and regulatory compliance, the future of blockchain in transforming these sectors is bright. As we move towards this future, it will be crucial for businesses, governments, and individuals to understand and adapt to the opportunities and changes brought about by this groundbreaking technology.
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Data Center, Generative AI
 Mastering Data Science with SQL: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals
Mastering Data Science with SQL: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals
International Dublin University
November 27, 2023
1. Introduction
Data science has emerged as a critical field in today's digital age, with organizations relying on data-driven insights to make informed business decisions. At the heart of this field lies SQL, the programming language used for managing and manipulating large datasets. Mastering SQL is essential for any professional looking to excel in the world of data science.
This comprehensive guide will provide professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to become proficient in SQL, from basic querying to advanced database management. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced data scientist, this guide will take your SQL abilities to the next level. Get ready to unlock the full potential of data science with SQL!
2. The power of SQL in data science
As a data scientist, understanding the power of SQL is crucial for unlocking the full potential of data science. SQL (Structured Query Language) is the backbone of data management and manipulation, allowing professionals to extract, manipulate, and analyze data from large datasets efficiently.
One of the key advantages of using SQL in data science is its ability to handle massive amounts of data swiftly. With SQL, you can perform complex queries and join multiple tables to extract the information you need, even from terabytes of data.
Furthermore, SQL provides a common language for data scientists to communicate and collaborate with other stakeholders such as database administrators and software engineers. This shared language ensures seamless integration of data science projects within an organization.
In addition, SQL offers a wide range of built-in functions and mathematical operations, making it a powerful tool for data analysis. From aggregating data to calculating statistics, SQL provides a comprehensive set of functionalities that can be used to derive meaningful insights from data.
Lastly, SQL is highly scalable, offering efficient performance even on large datasets. With its ability to optimize query execution and perform parallel processing, data scientists can work with massive datasets without sacrificing performance.
In summary, SQL empowers data scientists by providing a powerful and scalable tool for managing, manipulating, and analyzing data. By mastering SQL, professionals can enhance their data science skill set and contribute to impactful data-driven decisions.
3. SQL basics for professionals
In this section, we will cover the basic SQL concepts that every professional should be familiar with. Whether you are a beginner or have some experience with SQL, these fundamentals will serve as a solid foundation for your data science journey.
1. Understanding the structure of a database: Before diving into SQL, it is essential to grasp the concept of a database and its components. We will explore the different types of databases, tables, and data types commonly used in SQL.
2. Querying data: One of the primary purposes of SQL is to query data from databases. We will learn how to write basic SQL queries to retrieve data from a single table. From selecting specific columns to filtering rows based on conditions, you will gain the skills to extract the information you need.
3. Joining tables: Often, data resides in multiple tables that are linked through common fields. We will cover different types of joins, such as inner join, left join, right join, and outer join, to combine data from multiple tables efficiently.
4. Filtering and sorting data: In data science, finding and manipulating data based on specific criteria is essential. We will learn how to use WHERE and ORDER BY clauses to filter and sort data, respectively.
5. Aggregating data: Aggregating data allows us to summarize information and gain insights from large datasets. We will explore SQL functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX to calculate summary statistics.
By mastering these SQL basics, you will be equipped with the necessary skills to handle data efficiently and effectively in your data science projects. So let's dive in and explore the world of SQL!
4. Advanced SQL techniques for data analysis
Now that you have a strong foundation in the basics of SQL, it's time to take your data science skills to the next level with advanced SQL techniques for data analysis. In this section, we will explore some powerful SQL concepts and functions that will enable you to extract valuable insights from your data.
1. Subqueries: Subqueries are queries nested within other queries, and they allow you to perform more complex operations on your data. We will learn how to use subqueries to make calculations, create custom columns, and filter data based on multiple conditions.
2. Window functions: Window functions provide a way to perform calculations across a set of rows in a table, allowing you to compute aggregations and rankings within specific groups or partitions. We will dive into the syntax and usage of window functions, including popular functions like ROW_NUMBER, RANK, and LEAD.
3. Advanced joins: While you've already learned the basics of joining tables, there are more advanced techniques that can be useful in data analysis. We will cover topics such as self-joins, cross joins, and conditional joins to handle complex data relationships effectively.
4. Handling missing data: Dealing with missing or null values is a common challenge in data analysis. We will explore techniques to handle missing data, such as using the COALESCE function, NULLIF function, and advanced CASE statements.
5. Optimizing SQL queries: As your data grows, performance becomes crucial. We will discuss strategies for optimizing SQL queries, including indexing, query tuning, and understanding query execution plans.
By mastering these advanced SQL techniques, you will be able to manipulate and analyze your data more effectively, making informed decisions and extracting meaningful insights. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the world of data science with SQL!
5. Integrating SQL with other data science tools
In addition to mastering advanced SQL techniques, integrating SQL with other data science tools is essential for professionals looking to excel in the field. While SQL is a powerful language for data manipulation and analysis, it is often used in conjunction with other tools to enhance its capabilities.
1. Python integration: Python is a popular programming language for data science due to its extensive libraries and flexibility. By integrating SQL with Python, you can leverage the strengths of both languages. You can use Python libraries such as pandas to manipulate and analyze data retrieved from SQL databases. Additionally, you can execute SQL queries from within Python to fetch data and perform complex calculations.
2. R integration: Similar to Python, R is another widely used language in data science. It has a rich ecosystem of packages specifically designed for statistical analysis and data visualization. By integrating SQL with R, you can import data from SQL databases into R, perform statistical analyses, and create visually appealing plots and charts.
3. Visualization tools: Data visualization plays a vital role in data analysis, as it helps in understanding patterns and trends within the data. Integration of SQL with popular visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or Looker allows you to create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations directly from your SQL queries.
4. Machine learning libraries: Machine learning is a key component of data science, enabling predictive modeling and pattern recognition. By integrating SQL with popular machine learning libraries like scikit-learn or TensorFlow, you can train and deploy machine learning models using data extracted from SQL databases.
By integrating SQL with these complementary tools, you can unlock the full potential of your data and gain deeper insights that go beyond traditional SQL capabilities. In the next section, we will explore how to seamlessly integrate SQL with these tools and showcase some practical examples of their usage. Stay tuned!
6. Best practices for optimizing SQL queries
Efficiently writing and optimizing SQL queries is crucial for professionals in the field of data science. By following best practices, you can significantly improve the performance of your queries and enhance your overall data analysis process.
1. Indexing: Indexing is one of the most effective ways to optimize SQL queries. By creating indexes on columns frequently used in WHERE clauses or JOIN conditions, you can speed up query execution time. It is important to carefully analyze your data and choose the columns that are most suitable for indexing.
2. Minimize the use of unnecessary functions and expressions: Functions and expressions in SQL queries can slow down performance, especially when used on large datasets. Whenever possible, avoid using unnecessary functions or expressions and simplify your queries to improve efficiency.
3. Use appropriate join types: Choosing the right join type can have a significant impact on query performance. Understand the differences between different join types such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, and RIGHT JOIN, and select the most appropriate join type based on your data and query requirements.
4. Apply query optimization techniques: SQL databases often provide tools and techniques for optimizing queries. Utilize features like query hints, query plans, and query optimization tools provided by your database management system. These tools can help you identify and resolve performance bottlenecks in your queries.
5. Monitor and tune query performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your SQL queries and identify any potential performance issues. Use tools like database profiling and query analysis to identify bottlenecks and optimize your queries accordingly.
By following these best practices, you can optimize the performance of your SQL queries and streamline your data analysis workflow. In the next section, we will delve deeper into each of these best practices and provide practical examples to illustrate their application. Stay tuned!
7. Real-world applications of SQL in data science
:
In addition to optimizing SQL queries, it is essential to understand the real-world applications of SQL in data science. SQL is a powerful tool that enables professionals to extract valuable insights from large datasets. Let's explore some common applications of SQL in data science:
a. Data Cleaning and Transformation: SQL can be used to clean and transform messy datasets, ensuring data consistency and accuracy. With SQL, you can eliminate duplicate records, handle missing values, and format data for further analysis.
b. Data Aggregation and Summarization: SQL allows professionals to aggregate and summarize data efficiently. By leveraging functions like GROUP BY, COUNT, SUM, and AVG, you can generate meaningful summaries and gain valuable insights from your data.
c. Data Exploration and Visualization: SQL can be used to explore and visualize data, helping professionals identify patterns and trends. By joining tables, filtering data, and applying statistical functions, you can generate meaningful visualizations that aid in decision-making.
d. Predictive Analytics: SQL can also be used for predictive analytics tasks. By combining SQL with statistical functions and machine learning techniques, professionals can build predictive models, make forecasts, and identify trends in their data.
e. Reporting and Dashboarding: SQL enables professionals to generate reports and build interactive dashboards. With SQL, you can create dynamic visualizations and share your insights with stakeholders in a user-friendly format.
Understanding these real-world applications of SQL in data science will empower you to leverage its capabilities effectively. In the following section, we will delve deeper into each of these applications and provide practical examples to showcase their significance.
8. Conclusion: Becoming a SQL master in the world of data science
In conclusion, mastering SQL is crucial for professionals in the field of data science. With its ability to optimize queries and its wide range of real-world applications, SQL is a powerful tool for extracting valuable insights from datasets. From data cleaning and transformation to predictive analytics and reporting, SQL provides professionals with the means to explore, analyze, and visualize data effectively.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into each of these applications and provide practical examples to showcase their significance. By understanding and applying these concepts, you will be well on your way to becoming a SQL master in the world of data science. So, let's roll up our sleeves and dive deep into the various applications of SQL in data science and how they can be leveraged to gain a competitive edge in the industry. Stay tuned for more insights and practical tips!
See publication
Tags: Blockchain, Design Thinking, Data Center
 Awarded from IATA for Foundation in travel and Tourism
Awarded from IATA for Foundation in travel and Tourism
 FedEx Leadership program Certification
FedEx Leadership program Certification
 Globalization
Globalization
 Industry effects on city logistic
Industry effects on city logistic
 The Role of AI in Enhancing Daily Work Life
The Role of AI in Enhancing Daily Work Life
 GAP Nedir?
GAP Nedir?
 encryption techniques
encryption techniques
 Blockchain's Revolutionary Impact on Traditional Industries and Its Adoption Challenges
Blockchain's Revolutionary Impact on Traditional Industries and Its Adoption Challenges
 Navigating the World of Academic Journal Publication: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the World of Academic Journal Publication: A Comprehensive Guide
 The Future of Wearable Technology: Smart Glasses by Ray-Ban and Meta
The Future of Wearable Technology: Smart Glasses by Ray-Ban and Meta
 The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Everyday Tasks: A Statistical Overview
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Everyday Tasks: A Statistical Overview
 The Future of Shopping: How AI Will Shape Our Purchases
The Future of Shopping: How AI Will Shape Our Purchases
 “The Transformative Power of Blockchain in the Global Economy”
“The Transformative Power of Blockchain in the Global Economy”
 Managing Big Data with SQL and Databases
Managing Big Data with SQL and Databases
 Navigating the Horizon: The Future of AI and Its Impact on Humanity
Navigating the Horizon: The Future of AI and Its Impact on Humanity
 Latest inventions in the marketing
Latest inventions in the marketing
 What is the Scrum
What is the Scrum
 The Daily Integration of AI: Transforming Lives and Industries
The Daily Integration of AI: Transforming Lives and Industries
 Unveiling the Convergence: Data and Blockchain Technologies
Unveiling the Convergence: Data and Blockchain Technologies
 The Dawn and Future Horizon of Artificial Intelligence: A Journey from Simple Algorithms to Advanced AI
The Dawn and Future Horizon of Artificial Intelligence: A Journey from Simple Algorithms to Advanced AI
 a review on visual programming book
a review on visual programming book
 The Power of Unity: Collaborative Data Sharing in the Digital Age
The Power of Unity: Collaborative Data Sharing in the Digital Age
 Project and Development Manager
Project and Development Manager
 Quality Driven Management build
Quality Driven Management build
 Quality Driven Management-Evaluate
Quality Driven Management-Evaluate
 Quality Driven Management-Launch
Quality Driven Management-Launch
 The Unstoppable Rise of Artificial Intelligence: A Revolution in Progress
The Unstoppable Rise of Artificial Intelligence: A Revolution in Progress
 The Future of Generative AI: Transforming the Way We Create and Interact
The Future of Generative AI: Transforming the Way We Create and Interact
 The Expansive Future of Blockchain Across Industries
The Expansive Future of Blockchain Across Industries
 Mastering Data Science with SQL: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals
Mastering Data Science with SQL: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals
 The impact of Generative AI on jobs and the economy is a topic of ongoing research and discussion. The conclusions drawn from various studies and expert opinions suggest both challenges and opportunities.
The impact of Generative AI on jobs and the economy is a topic of ongoing research and discussion. The conclusions drawn from various studies and expert opinions suggest both challenges and opportunities.
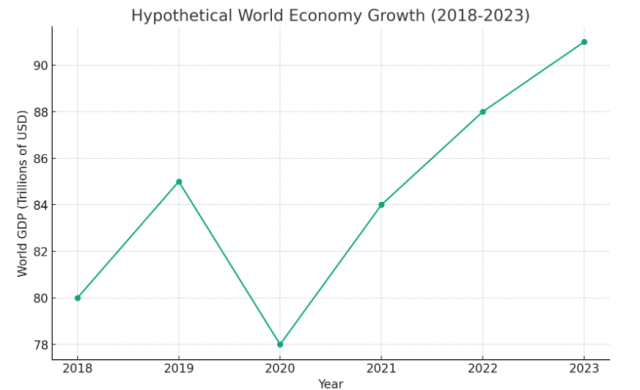 Here is a hypothetical graph illustrating the growth of the world economy from 2018 to 2023.
Here is a hypothetical graph illustrating the growth of the world economy from 2018 to 2023.

 Verinin AI gelişimindeki rolünü üç ana başlık altında inceleyeceğiz: veri hacmi ve çeşitliliği, veri kalitesi ve işlenmesi, ve etik ve gizlilik konuları
Verinin AI gelişimindeki rolünü üç ana başlık altında inceleyeceğiz: veri hacmi ve çeşitliliği, veri kalitesi ve işlenmesi, ve etik ve gizlilik konuları
 Title: The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Daily Human Routines
Title: The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Daily Human Routines
 A mobility blog typically focuses on various aspects of transportation, including cars, bikes, public transit, electric vehicles (EVs), and other modes of getting from one place to another. These blogs often cover a wide range of topics related to mobility, such as
A mobility blog typically focuses on various aspects of transportation, including cars, bikes, public transit, electric vehicles (EVs), and other modes of getting from one place to another. These blogs often cover a wide range of topics related to mobility, such as
 The Future of Work: Emerging Job Opportunities in the AI Era
The Future of Work: Emerging Job Opportunities in the AI Era
 The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: The Role of Data
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: The Role of Data
 Unlocking the Power of Data: Understanding the Importance of Generative AI
Unlocking the Power of Data: Understanding the Importance of Generative AI
 About Blockchain
About Blockchain