Jan31

The accelerated penetration of digital business and the adoption of cloud computing and related technologies including IoT, AI, big data, and DevOps go hand in hand with the ever-increasing cyber threats inflation. As paradoxical as this may sound, the adoption of these technologies and the IT transformations that go with it introduce new security vulnerabilities. The best answer is certainly not the isolated implementation of the latest tools as is too often the case, but the deployment of what is increasingly referred to as Enterprise Cloud Security. It makes business leaders both proactive and responsive to cyberattacks. In the following, I discuss the Cybersecurity Fortress Design Pattern that I developed to implement enterprise cloud security.
Enterprise Cloud Security refers to how well people, policies, procedures, processes and security tools are deployed throughout the organization in a way that effectively protects the company's IT including cloud and on-premise operations, critical systems and data from internet attacks. Despite the fact that cloud security and in general cybersecurity has become a key business issue, an impressive number of companies that have adopted cloud computing have experienced cloud-related security incidents, about 80% of them, according to many well-informed reports.
The most common cloud security incidents according to CloudTech's Duncan MacRae in a study that involved a panel of major cloud adopters include:
I totally agree with the findings, they are the same as I have been observing for 13 years. My conviction is that the root cause of these cloud security issues is the fact that systemic and holistic approaches to managing cybersecurity are ignored in favor of piecemeal processes. It is why I developed the Cybersecurity Fortress Design Pattern.
The cybersecurity fortress design pattern seeks to help businesses to rapidly implement robust cyber fortresses. It builds on the NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF) to provide the methodological, operational, and organizational framework needed to effectively manage cybersecurity risks and proactively prevent or respond to cyberattacks.
The cybersecurity fortress pattern is based on five principles that determine the mindset as well as the organizational, operational, and technological pillars needed to design and implement cybersecurity fortresses. They include:
The design of enterprise cloud security fortresses should follow these five principles.
The above figure gives an overview of the enterprise cloud architecture and how cybersecurity fits into the company's IT. It highlights five cybersecurity building blocks derived from the NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF) five core functions including Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Each encapsulates specific cybersecurity processes, activities, staff, skills, methodologies, and tools.
Let's discuss them further!
Identify - In connection with principles 1, 2, and 3, the challenge here is to deploy a system of people, processes, and tools that allows the company to have a 360 degree view of its enterprise architecture and IT infrastructure so that it is able to proactively spot and evaluate cyber risks and determine preventive actions. The bottom line is to get current and future threats, both internal and external, clearly identified and documented. Key activities in this building block include governance, asset management, and risk management.
Protect - Relating to principles 4 and 5, the core purpose in this building block is to perform preventive cybersecurity controls in well-determined human, organizational, operational, and technological circumstances. The focus is on identity management and access controls and what's expected is to get remote access controlled. Key activities include identity management and access control, awareness and training, data security, information security protection processes and procedures, maintenance. Popular Preventive Solutions (procedures, policies, controls and tools) supporting this building block's activities include Authentication & Authorization, Firewalls, Malware Protections, VPN, MFA, SSO, and Cryptography.
Detect - Relating to principle 4 as well, this building block stresses security continuous monitoring through performance of detective cybersecurity controls in well-determined human, organizational, operational, and technological contexts. The objective is to get vulnerabilities scans continuously performed. Key activities include security continuous monitoring and anomalies and events continuous based on detection processes. Common Detective Solutions (procedures, policies, controls and tools) supporting the Detect building block include Events and Anomalies Monitoring, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Security Information and Event Management Systems (SIEMs), User and Entity Behavior Analytics Systems (UEBAs), Threat Hunting Systems, and Antivirus Software.
Respond - Addressing principles 4 and 5, the focal point in this building block is to perform reactive cybersecurity controls following analysis and understanding cyber attack contexts. The goal is to make sure forensics are performed. Key activities include analysis, response planning, communications, mitigations, and improvements. Usual Reactive Solutions (procedures, policies, controls and tools) include Incident Response Plan (IRP), Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT), and IDS Logs Analysis Tools.
Recover - In connection with principles 4 and 5, this building block is concerned with recovering from cyberattacks. The bottom line is to get recovery plans executed as needed. Key activities include recovery planning, communications, and improvements. Familiar Recovery Solutions (procedures, policies, controls and tools) include Recovery Plans, Disaster Recovery, and Backup & Recovery.
Those familiar with it has probably guessed that deploying enterprise cloud security is about implementing the NIST CSF recommendations.
Implementing the organizational, operational and technological framework in which technical experts will express their ingenuity to protect the company's assets is the first thing you must have in mind. It is the purpose of the 4 stages of the Cybersecurity Fortress Pattern:
The goal in this step is to identify and understand the gaps between the as-is environment and the enterprise cloud security architecture from the cybersecurity fortress pattern's perspectives. Key activities include (1) putting together the as-is enterprise architecture including people, processes, methodologies and tools; (2) benchmarking the as-is enterprise architecture against the cybersecurity fortress architecture elements; (3) identifying the gaps along with the related vulnerabilities; and (4) making cybersecurity improvement recommendations.
The stake in this step is to fill the gaps identified in the audit to design the to-be enterprise cloud security platform and align it, as much as possible, to the agreed upon cybersecurity fortress pattern's recommendations. Primary activities include (1) identifying / designing cybersecurity solutions likely to fill the identified gaps; (2) reconfiguring the as-is cybersecurity architecture into the to-be cybersecurity architecture from the people, processes, procedures, policies, and tools perspective; and (3) develop the cybersecurity fortress deployment plan.
In this step the goal is to deploy your cybersecurity people, processes, procedures, policies, and tools throughout your organization. The principal activities include (1) communicating about the changes ahead, (2) training to the to-be cybersecurity responsibility assignment (RACI) matrix, processes, procedures, policies, and tools across the organization; and (4) running a cybersecurity pilot project.
The ever-increasing number of cyberattacks, +38% in 2022 compared to 2021, leaves no room for improvisation; CIOs would be wrong to persist in blind cybersecurity implementations that stress blind deployments of tools. Furthermore, their incredible plurality and accelerated frequency make it suicidal to cling to this one-eyed view of cybersecurity. Enterprise architecture approaches are required as they provide the tools (cartography of applications, systems, and processes, enterprise architecture governance, etc) that help to make the implementation of cyber fortresses easier and faster.
Additional benefits of the fortress design pattern include:
Stay tuned, I will soon launch the initiative, The AWS Cybersecurity Fortress Project. In the same spirit as my book "Transforming Your Business with AWS," this international community of experts that we will build together will share Enterprise Cloud Security best practices with a view to deliver a formal and complete AWS Cybersecurity Fortress Models.
Keywords: Cloud, Cybersecurity, Business Continuity
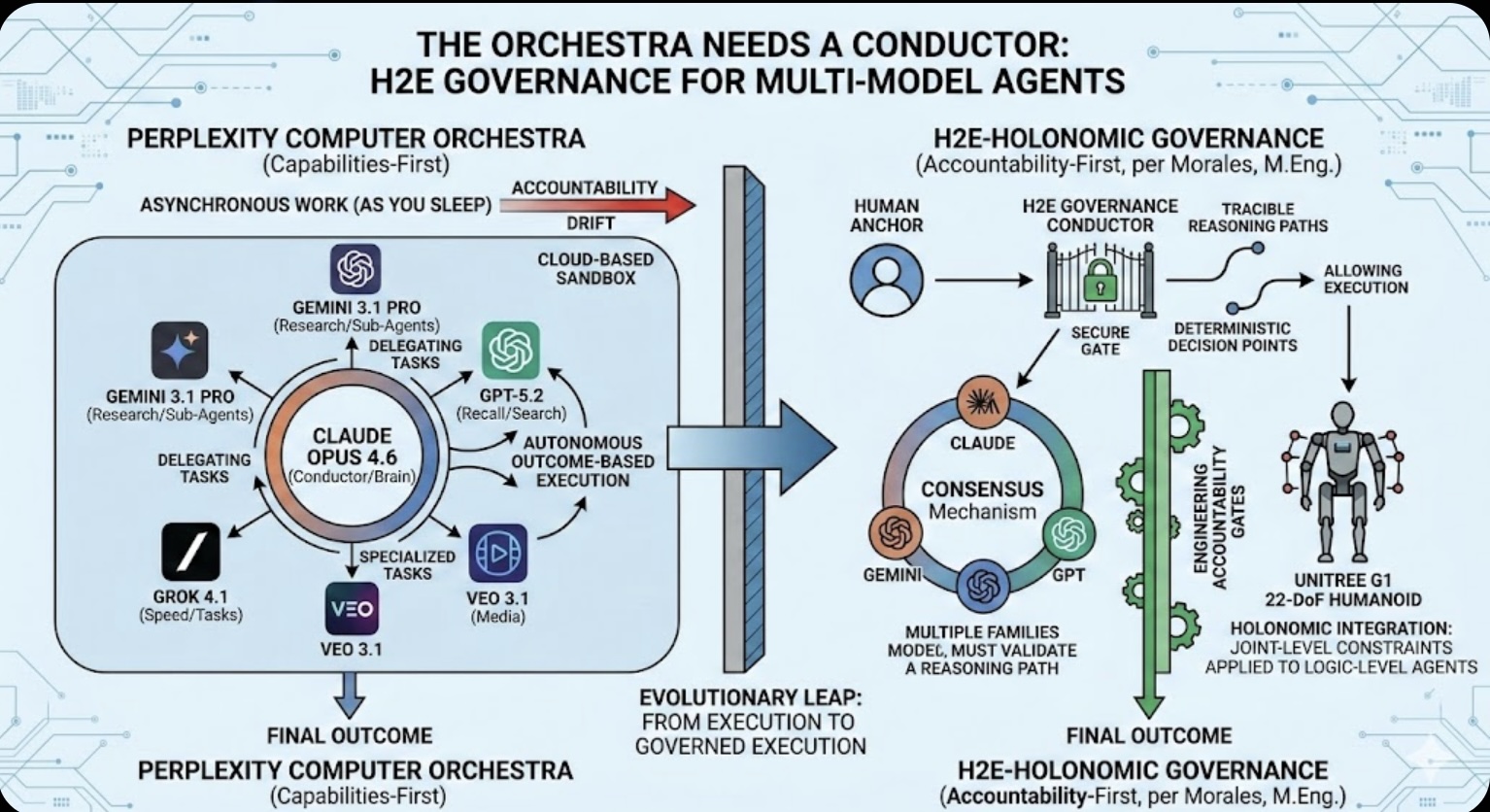 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business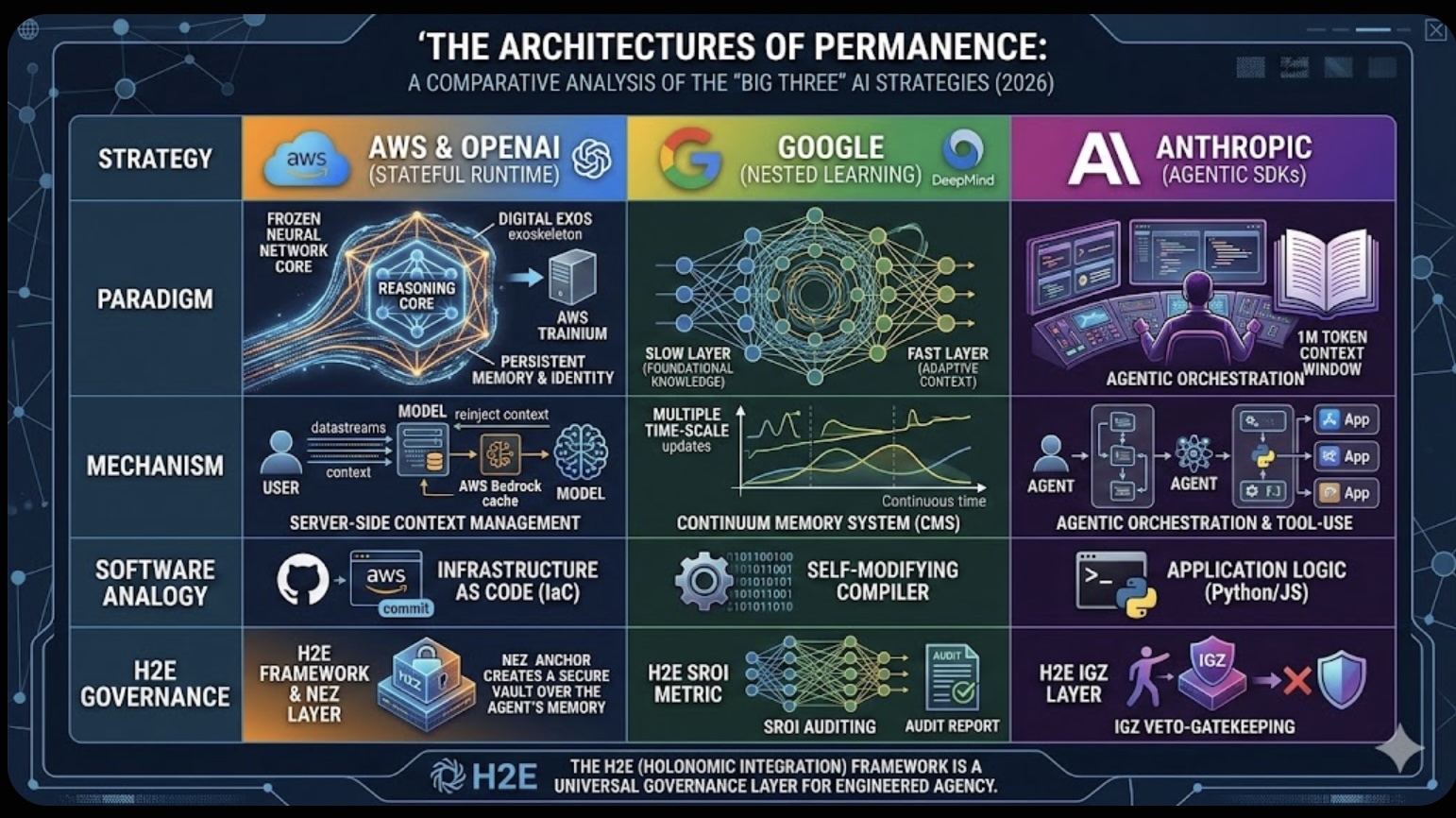 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026