Aug21

Analytics is interesting -- technical people who use it often feel imposter syndrome, non-technical people who encounter it often think it's magic, and both sides often feel overwhelmed at the possibilities.
Here are 20 different types of Analytics, use case, and example to make it all more approachable:
1. Descriptive Analytics
Purpose: Provides insights into past events by summarizing historical data.
Example: Reporting on monthly sales figures, website traffic, or customer demographics.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Purpose: Explores data to understand the reasons behind past performance or outcomes.
Example: Identifying why sales dropped in a particular region or why customer churn increased.
3. Predictive Analytics
Purpose: Uses statistical models and machine learning to forecast future events based on historical data.
Example: Predicting future sales trends, customer behavior, or demand for products.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
Purpose: Recommends actions or strategies to optimize outcomes based on predictive analytics.
Example: Suggesting pricing strategies, inventory management, or marketing campaigns.
5. Cognitive Analytics
Purpose: Mimics human thought processes to provide more nuanced insights, often using AI and natural language processing.
Example: Chatbots that understand and respond to customer queries or systems that make personalized product recommendations.
6. Real-Time Analytics
Purpose: Analyzes data as it is generated to provide immediate insights and enable quick decision-making.
Example: Monitoring real-time stock prices, website traffic, or social media mentions.
7. Exploratory Analytics
Purpose: Involves investigating datasets to uncover patterns, trends, or relationships without specific hypotheses.
Example: Identifying new market segments or discovering unexpected correlations in customer data.
8. Inferential Analytics
Purpose: Uses statistical methods to make inferences or generalizations about a population based on sample data.
Example: Conducting A/B testing to infer which version of a product or campaign performs better.
9. Diagnostic Analytics
Purpose: Explores historical data to find the root causes of past outcomes or issues.
Example: Investigating why a marketing campaign underperformed by analyzing customer engagement data.
10. Operational Analytics
Purpose: Focuses on improving efficiency and optimizing business processes through real-time data analysis.
Example: Analyzing production line data to reduce downtime or optimizing logistics routes.
11. Behavioral Analytics
Purpose: Studies customer behavior to understand how they interact with products or services.
Example: Tracking user journeys on a website to improve user experience or increase conversions.
12. Text Analytics (or Text Mining)
Purpose: Analyzes unstructured text data (e.g., emails, social media posts) to extract meaningful information.
Example: Sentiment analysis of customer reviews or analyzing open-ended survey responses.
13. Visual Analytics
Purpose: Combines data visualization with analytics to help users understand complex data through visual representations.
Example: Interactive dashboards that allow users to explore data trends and correlations.
14. Spatial Analytics
Purpose: Analyzes geographical or spatial data to understand location-based patterns and trends.
Example: Analyzing retail store performance by location or optimizing delivery routes based on geography.
15. Network Analytics
Purpose: Analyzes relationships and interactions within networks, such as social networks or supply chains.
Example: Identifying influencers in a social network or detecting bottlenecks in a supply chain.
16. Risk Analytics
Purpose: Assesses and quantifies risks to help organizations manage and mitigate them.
Example: Evaluating credit risk for loan approvals or assessing financial risk in investment portfolios.
17. Customer Analytics
Purpose: Focuses on understanding customer preferences, behavior, and lifetime value.
Example: Segmenting customers based on purchasing behavior or predicting customer churn.
18. Web Analytics
Purpose: Analyzes web traffic data to understand user behavior and optimize website performance.
Example: Tracking page views, bounce rates, and conversion rates to improve site design.
19. HR Analytics (or People Analytics)
Purpose: Analyzes workforce data to improve human resource management and employee performance.
Example: Identifying factors that contribute to employee retention or predicting future hiring needs.
20. Financial Analytics
Purpose: Analyzes financial data to support budgeting, forecasting, and financial decision-making.
Example: Analyzing cash flow trends or forecasting revenue growth.
Hopefully that cleared things up!
By Dan Banas
Keywords: AI, Analytics, Business Strategy
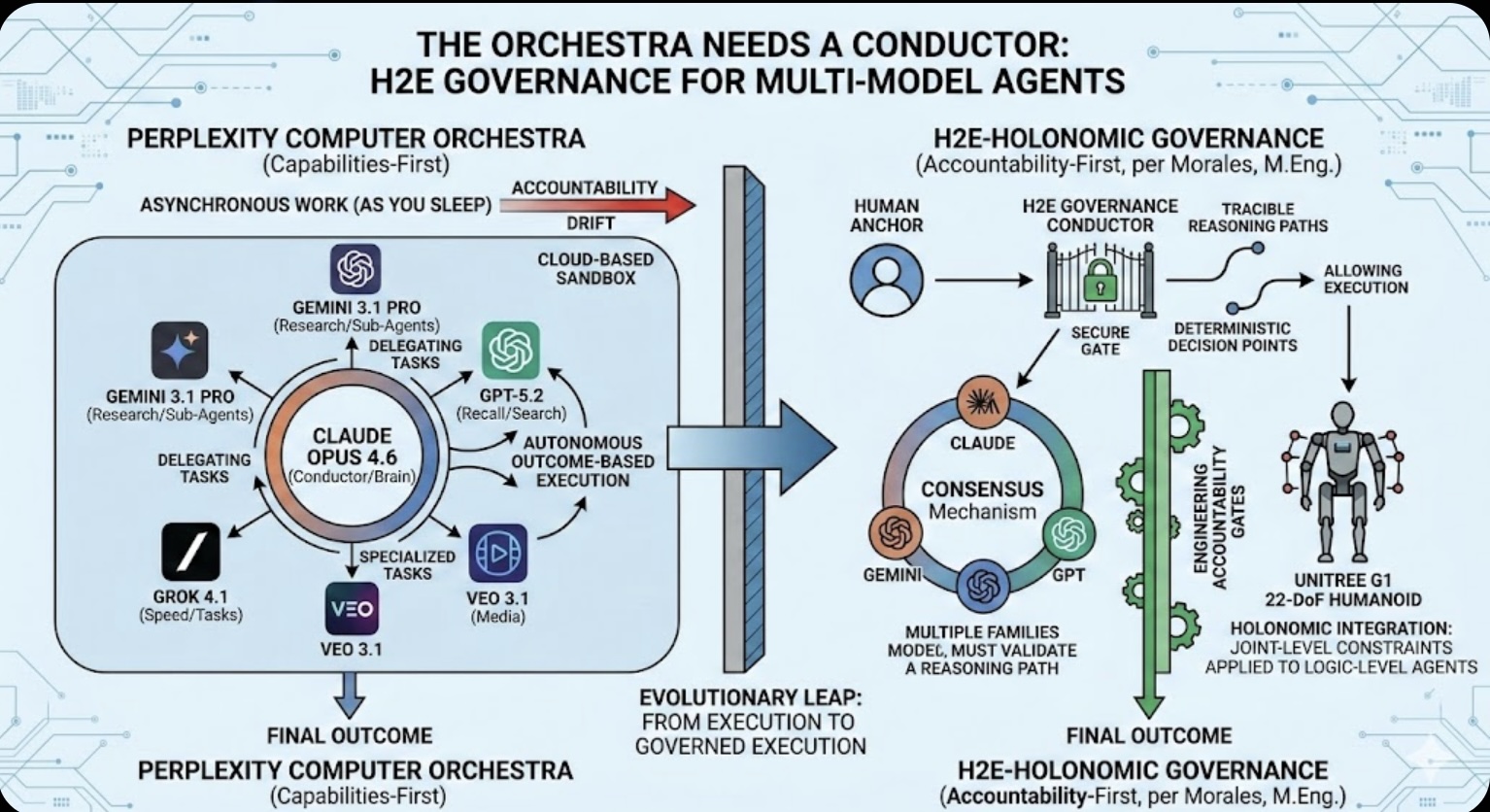 The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance
The Orchestra Needs a Conductor: Why Multi-Model Agents Require H2E Governance The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business
The Role of Memory in Modern-day Business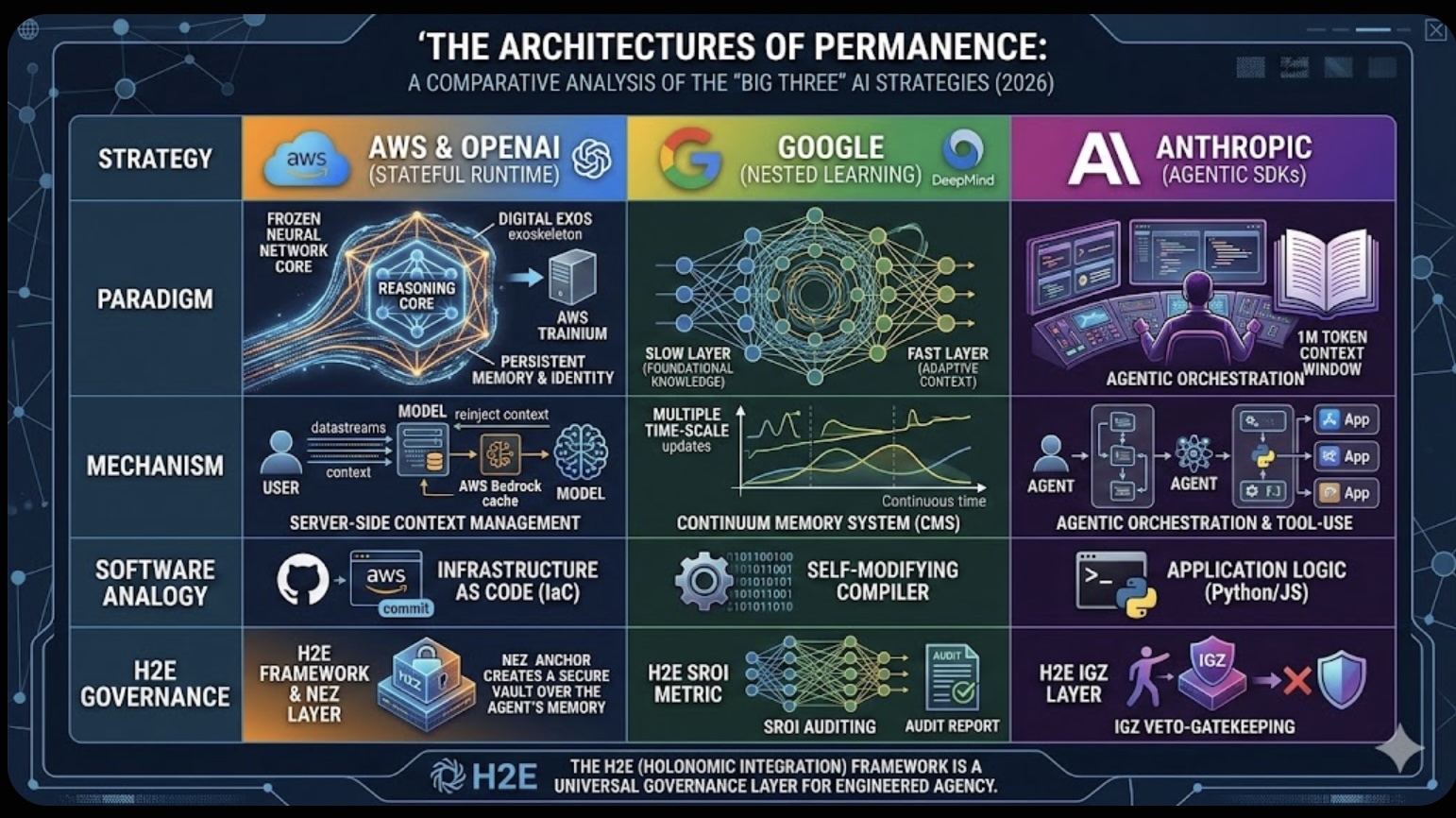 The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026)
The Architectures of Permanence: A Comparative Analysis of the "Big Three" AI Strategies (2026) Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement
Friday’s Change Reflection Quote - Leadership of Change - Change Leaders Enable Generational Advancement The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026
The Corix Partners Friday Reading List - February 27, 2026