 Connections Between Drama Education and the Digital Education Revolution
Connections Between Drama Education and the Digital Education Revolution
2010 DramaWest State Conference
August 01, 2022
Drama Education has long been regarded one of the most innovative and critically aware areas of contemporary pedagogy. With the increasing emphasis on the role of technology in education and the tremendous injection of funds towards deploying technology within the K‐12 sector, Drama is charged with considering the ways in which it will embrace the challenges of the net generation.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Education
 Stepping into the virtual—is virtuality a contemporary alternative to drama
Stepping into the virtual—is virtuality a contemporary alternative to drama
IDEA Special Interest Fields of Drama, Theatre and Education. Brisbane: IDEA Publications
August 01, 2022
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
 Drama and technology: The pursuit of uncertain benefits
Drama and technology: The pursuit of uncertain benefits
Drama Queensland Says
August 01, 2022
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
The internet as a dramatic medium
Interactive and improvisational drama: varieties of applied theatre and performance. Bloomington, IN.: iUniverse
August 01, 2022
The internet has become a virtual meta-stage on which millions of people are role playing a variety of characters, interacting with others in adventures! In recent years, numerous internet and virtual processes seem to partake of elements of theatre, role-play games, and collective performance art, so that this kind of interactivity should also be recognized as an extension or category of theatre.(The editor was ambivalent about including this chapter, but wondered if the generation raised on these games might see it as being an obvious and necessary inclusion.)
What kind of drama is involved in the role-playing games available over the Internet? Software has been developed that allows people to interact with others, not only in games, but also in drama-like performances. In this chapter, these applications will be noted, with some emphasis being give to the kinds of processes that seem to be operating in the service of social or personal change.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech
Education for Sustainable Development: A Study in Adolescent Perception Changes Towards Sustainability Following a Strategic Planning-Based Intervention—The Young Persons’ Plan for the Planet Program
Sustainability, MDPI
August 01, 2022
In 2016, the United Nations (UN) launched the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as a framework for sustainable development and a sustainable future. However, the global challenge has been to engage, connect, and empower communities, particularly young people, to both understand and deliver the 17 SDGs. In this study, we show the benefit of a strategic planning-based experiential learning tool, the Young Persons’ Plan for the Planet (YPPP) Program, to improve the underlying competencies of Australian and Mauritian adolescents in increasing understanding and delivering the SDGs. The study was conducted with 300 middle to senior high school students, in 25 schools throughout Australia and Mauritius, over an 18-month period. The intervention included the development of research, strategic planning, management, STEM (Science Technology, Engineering, Maths) and global competency skills in the students, to enable them to build and deliver regional and national SDG plans. Research methods included pre- and post-intervention testing of the attitudes of these students to sustainable development outcomes and compared these attitudes to subsets of scientists and the Australian national population. Our results, from both qualitative and quantitative evidence, demonstrate significant improvements in these adolescents’ appreciation of, and attitudes towards, the SDGs and sustainable outcomes, across a range of key parameters. The results from the 76 students who attended the International Conference in Mauritius in December 2018 demonstrate significant improvements in mean levels of understanding, and attitudes of the students towards the SDGs awareness (+85%), understanding/engagement (+75%), motivation (+57%), and action orientation/empowerment (+66%). These changes were tested across a range of socio-demographic, geographic, and cultural parameters, with consistent results. These findings have significant implications for the challenge of sustainable education and achieving community engagement and action towards the SDGs in Australia and Mauritius, particularly for young people. As the intervention can be replicated and scaled, the findings also highlight the opportunity to extend both the research and this type of experiential learning intervention across both broader geographies and other generation and community segments.
See publication
Tags: EdTech, Future of Work, Sustainability
 Digital Badges in Education
Digital Badges in Education
Springer
August 01, 2022
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, Education
 Advancing Mobile Learning in Formal And Informal Settings via Mobile App Technology: Where to From Here, and How?
Advancing Mobile Learning in Formal And Informal Settings via Mobile App Technology: Where to From Here, and How?
International Forum of Educational Technology & Society, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan
August 01, 2022
In this paper a brief review of the framework that addressed mobile learning implementation challenges (pedagogical, technological, policy and research) that was developed by Khaddage et al. (2015) is briefly discussed, followed by possible solutions that could be deployed to tackle those challenges. A unique approach is then applied to bridge the gap between formal and informal learning via MAT (Mobile Applications Technology). This approach is based on STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Art and Mathematics) as subjects to be taught and the specific skills needed to achieve the RLOC (Required Learning Outcome) that can support student learning informally. This specific approach shows HOW to advance mobile learning in formal and informal settings.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech
 A Philosophy of Open Digital Badges
A Philosophy of Open Digital Badges
Springer
August 01, 2022
One of the most promising educational technology tools, open digital badges, is quickly changing curricula, job acquisition, and workforce credentialing. Learning data, assessments, and expert validation made accessible in social media create a transparency that may well be suited for critical questions in education. Operating from a framework of establishing how badges are currently employed in learning—the influential contexts of individuals and communities, and data aggregation—raises questions concerning the roles of instructors, badge providers, and learning management systems. This “philosophy” of digital badges addresses a variety of epistemological concerns including the intersection of challenges to conventional educational motivation, suggestions of how Platonic and modern models of education are complementary, and implications of how badges may represent postmodern credentialing systems. These concerns are framed around understanding how current work in digital badges can feasibly transform learning; this is both an acknowledgment of how badges are beginning to change ecosystems of informal and formal learning as well as an attempt to demonstrate how an epistemological philosophy of badges can change educators’ thinking and accelerate innovation.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, Digital Disruption, EdTech
 Virtual worlds in Australian and New Zealand higher education: Remembering the past, understanding the present and imagining the future
Virtual worlds in Australian and New Zealand higher education: Remembering the past, understanding the present and imagining the future
Electric Dreams - ascilite 2013 Conference Proceedings Sydney
August 01, 2022
3D virtual reality, including the current generation of multi-user virtual worlds, has had a long history of use in education and training, and it experienced a surge of renewed interest with the advent of Second Life in 2003. What followed shortly after were several years marked by considerable hype around the use of virtual worlds for teaching, learning and research in higher education. For the moment, uptake of the technology seems to have plateaued, with academics either maintaining the status quo and continuing to use virtual worlds as they have previously done or choosing to opt out altogether. This paper presents a brief review of the use of virtual worlds in the Australian and New Zealand higher education sector in the past and reports on its use in the sector at the present time, based on input from members of the Australian and New Zealand Virtual Worlds Working Group. It then adopts a forward-looking perspective amid the current climate of uncertainty, musing on future directions and offering suggestions for potential new applications in light of recent technological developments and innovations in the area.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
 How are Australian higher education institutions contributing to change through innovative teaching and learning in virtual worlds?
How are Australian higher education institutions contributing to change through innovative teaching and learning in virtual worlds?
Proceedings ASCILITE 2011: 28th Annual Conference of the Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education: Changing Demands, Chang
August 01, 2022
Over the past decade, teaching and learning in virtual worlds has been at the forefront of many higher education institutions around the world. The DEHub Virtual Worlds Working Group (VWWG) consisting of Australian and New Zealand higher education academics was formed in 2009. These educators are investigating the role that virtual worlds play in the future of education and actively changing the direction of their own teaching practice and curricula. 47 academics reporting on 28 Australian higher education institutions present an overview of how they have changed directions through the effective use of virtual worlds for diverse teaching and learning activities such as business scenarios and virtual excursions, role-play simulations, experimentation and language development. The case studies offer insights into the ways in which institutions are continuing to change directions in their teaching to meet changing demands for innovative teaching, learning and research in virtual worlds. This paper highlights the ways in which the authors are using virtual worlds to create opportunities for rich, immersive and authentic activities that would be difficult or not possible to achieve through more traditional approaches.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
 Sustaining the future through virtual worlds
Sustaining the future through virtual worlds
ascilite-Australian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education
August 01, 2022
Virtual worlds (VWs) continue to be used extensively in Australia and New Zealand higher education institutions although the tendency towards making unrealistic claims of efficacy and popularity appears to be over. Some educators at higher education institutions continue to use VWs in the same way as they have done in the past; others are exploring a range of different VWs or using them in new ways; whilst some are opting out altogether. This paper presents an overview of how 46 educators from some 26 institutions see VWs as an opportunity to sustain higher education. The positives and negatives of using VWs are discussed.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
Second life/simulation: online sites for generative play
Drama Education with Digital Technology - Continuum International Publishing Group
August 01, 2022
Most of these 3-D MUVEs are also bandwidth hungry and in some contexts, schools in Australia for example, the cost of this bandwidth consumption means these technologies are almost always locked away from general access. Despite these restrictions there are educational institutions the world over using these worlds in creative ways to sup-port learning. What begins to define these worlds as something beyond a ‘game’or ‘communication tool’is the way that users decide to think about and engage with (and within) the worlds.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
 New applications, new global audiences: Educators repurposing and reusing 3D virtual and immersive learning resources
New applications, new global audiences: Educators repurposing and reusing 3D virtual and immersive learning resources
ascilite 2015 Australasian Society for Computers in Learning and Tertiary Education
August 01, 2022
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Metaverse
 Drama and technology: Teacher attitudes and perceptions
Drama and technology: Teacher attitudes and perceptions
Edith Cowan University
August 01, 2022
Educational systems are continuing to prioritise the importance of technology in learning. Curriculum guidelines and frameworks from across the globe insist that all learning areas find ways to utilise appropriate technologies in the teaching learning process. Drama Education is one area where the use of technology seems to be quite limited. The study seeks to determine some emerging understanding of the perceptions and attitudes held by Drama teachers about the introduction of Interactive and Information Technology (Digital Environments) into classroom Drama practice. Of particular interest to this researcher is the seeming reluctance to engage with such technology. Drama educators from all levels of education were invited to complete the survey via email and the Drama Education: A Global Perspective website will contribute to the study. Since the study functions in an essentially interpretive and descriptive mode it was not expected that generalisations will be forthcoming, although there do emerge some relational understandings as well as implications and considerations for future introduction of so-called digital environments in Drama, and related issues such as resourcing, professional development, and pre-service training. Additionally, this study identifies areas of need and/or deficiency within school structures in relation to technology access and requirements for Drama educators. This is especially relevant to the Western Australian context as education sectors are engaged in curriculum improvement programs that necessitate cross-curricula and integrated practices.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Education
Designing Learning Experiences for the Future of Learning in the Digital Age: A Proposed Framework.
Current Issues in Education
August 01, 2022
While our understanding of how we learn has grown exponentially, our knowledge of how to incorporate these ideas when designing instruction has not. This paper proposes a new framework for designing learning experiences which build on existing instructional design models but also incorporates a deep understanding of humans, how we learn, what motivates us, what causes us to lose interest, and what instruction will get us to remember and use our knowledge. The learning experience design framework includes three parts which form a continuous cycle of development and improvement: planning, creating, and refining, all informed by key situational factors. While non-linear, each part is further divided into two sections to address both sides of designing a learning experience: the learning and the experience. These sections can guide anyone into designing better learning experiences for the future of …
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech
PD for ML in HE: Embedding mobile learning in a university context
Conference EdMedia+ Innovate Learning - Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE)
August 01, 2022
Mobile devices are becoming ubiquitous in university settings. While online learning using desktop and laptop device has seen significant growth over the last decade, the next decade will see an increased use of online learning via mobile devices such as tablets and phones. However, the spread of mobile learning in universities is patchy, and thought needs to be given to approaches that will foster widespread uptake. In this paper, we highlight the potential for mobile learning (ML) in higher education (HE) and the ways in which professional development (PD) can be enacted to develop guidelines for mobile learning and embed practices across an institution.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Education
 Interfacing: Drama, the arts and ICT
Interfacing: Drama, the arts and ICT
Login: The Newsletter of the Educational Computing Association of Western Australia
August 01, 2022
As more teachers and schools begin to incorporate learning technologies, information technology, and especially the Internet into classroom practice it seems that Drama teachers are left to find how they will adapt to the changing requirements of curriculum and to find effective ways to incorporate such technologies into Drama Education.
I have been involved in the exploration of potential uses of computers in Drama education for approximately 8 years and have witnessed what seems to a general unwillingness amongst Drama teachers to seriously adopt a wide range of technologies into their practice. I further believe that the uses of technology in Drama education have not been adequately explored and as such Drama teachers have few models from which to develop their own practice. There is also the belief that, as a result of a changing paradigm in Drama education, education systems and professional development providers (including pre-service training) may be overlooking the resource requirements and the requisite skilling of teachers in this area.
See publication
Tags: Digital Transformation, EdTech, Education


 A scholarship program for academic staff to develop exemplary online learning tasks
A scholarship program for academic staff to develop exemplary online learning tasks
 Connections Between Drama Education and the Digital Education Revolution
Connections Between Drama Education and the Digital Education Revolution
 Stepping into the virtual—is virtuality a contemporary alternative to drama
Stepping into the virtual—is virtuality a contemporary alternative to drama
 Drama and technology: The pursuit of uncertain benefits
Drama and technology: The pursuit of uncertain benefits
 Digital Badges in Education
Digital Badges in Education
 Advancing Mobile Learning in Formal And Informal Settings via Mobile App Technology: Where to From Here, and How?
Advancing Mobile Learning in Formal And Informal Settings via Mobile App Technology: Where to From Here, and How?
 A Philosophy of Open Digital Badges
A Philosophy of Open Digital Badges
 Virtual worlds in Australian and New Zealand higher education: Remembering the past, understanding the present and imagining the future
Virtual worlds in Australian and New Zealand higher education: Remembering the past, understanding the present and imagining the future
 How are Australian higher education institutions contributing to change through innovative teaching and learning in virtual worlds?
How are Australian higher education institutions contributing to change through innovative teaching and learning in virtual worlds?
 Sustaining the future through virtual worlds
Sustaining the future through virtual worlds
 New applications, new global audiences: Educators repurposing and reusing 3D virtual and immersive learning resources
New applications, new global audiences: Educators repurposing and reusing 3D virtual and immersive learning resources
 Drama and technology: Teacher attitudes and perceptions
Drama and technology: Teacher attitudes and perceptions
 Interfacing: Drama, the arts and ICT
Interfacing: Drama, the arts and ICT
 Learning with Purpose
Learning with Purpose
 Taking Learning Beyond the school gate
Taking Learning Beyond the school gate
 Taking Learning Beyond the School Gate
Taking Learning Beyond the School Gate
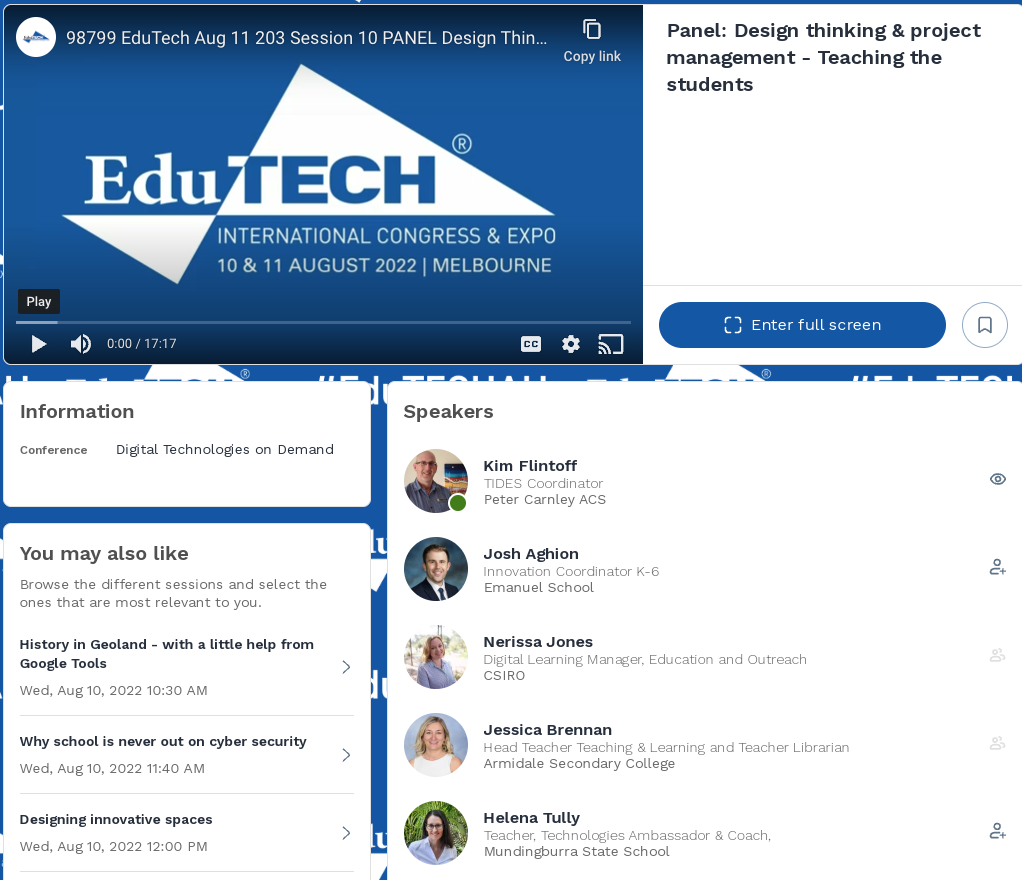 Design Thinking and Project Management
Design Thinking and Project Management
 The rising tide raises all vessels: learner development through the TIDES program.
The rising tide raises all vessels: learner development through the TIDES program.